6.2.6
Types of Synapse
Neuromuscular Junction
Neuromuscular Junction
A neuromuscular junction is a synapse between a motor neurone and a muscle cell. An action potential is transmitted across the synapse using the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. The steps involved are:


Arrival at the synaptic knob
Arrival at the synaptic knob
- An action potential arrives at the synaptic knob at the end of the motor neurone.
- The action potential depolarises the membrane of the synaptic knob. This causes voltage-gated calcium (Ca2+) ion channels to open.
- Ca2+ ions diffuse into the synaptic knob.


Release of acetylcholine (ACh)
Release of acetylcholine (ACh)
- The Ca2+ ion concentration inside the synaptic knob begins to increase.
- This causes the synaptic vesicles to move and fuse with the presynaptic membrane.
- Acetylcholine, the neurotransmitter inside the vesicles, is released into the synaptic cleft.
- This process is called exocytosis.


Binding to receptors
Binding to receptors
- Acetylcholine binds to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane called nicotinic cholinergic receptors.
- Binding of the neurotransmitter opens sodium ion channels in the postsynaptic muscle cell.
- As Na+ ions diffuse into the cell, the membrane becomes depolarised.
- If the potential difference reaches the threshold value, an action potential is generated and flows along the motor cell.


Removal of acetylcholine
Removal of acetylcholine
- An enzyme called acetylcholinesterase (AChE) breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft.
- The products of the break down are reabsorbed by the presynaptic neurone and reused to synthesise more acetylcholine.
- It is important that the acetylcholine is removed from the receptors. This stops action potentials from being continuously generated in the postsynaptic cell.
Cholinergic Synapses
Cholinergic Synapses
Synapses that use acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter are called cholinergic synapses. Although acetylcholine is also used at a neuromuscular junction, there are some key differences:


Type of postsynaptic cell
Type of postsynaptic cell
- Cholinergic synapses are between two neurones.
- Neuromuscular junctions are between a motor neurone and a muscle cell.


Number of receptors
Number of receptors
- There are less receptors in the postsynaptic membrane at a cholinergic synapse than at a neuromuscular junction.


Type of response
Type of response
- A cholinergic synapse can trigger an inhibitory or excitatory response in the postsynaptic membrane.
- An action potential at a neuromuscular junction always triggers an excitatory response in the muscle cell.
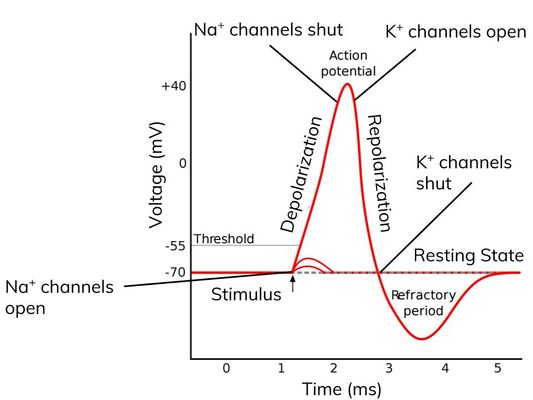

Result of depolarisation
Result of depolarisation
- In a cholinergic synapse, depolarisation of the postsynaptic membrane results in an action potential.
- At a neuromuscular junction, depolarisation of the postsynaptic membrane results in muscle contraction.
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase
- Acetylcholinesterase is the enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine after it has bound to the receptors on the postsynaptic membrane.
- In cholinergic synapses, the enzyme is located in the synaptic cleft.
- At a neuromuscular junction, the enzyme is stored in clefts in the postsynaptic membrane.
1Biological Molecules
1.1Monomers & Polymers
1.2Carbohydrates
1.3Lipids
1.4Proteins
1.4.1The Peptide Chain
1.4.2Investigating Proteins
1.4.3Primary & Secondary Protein Structure
1.4.4Tertiary & Quaternary Protein Structure
1.4.5Enzymes
1.4.6Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
1.4.7Enzyme-Controlled Reactions
1.4.8End of Topic Test - Lipids & Proteins
1.4.9A-A* (AO3/4) - Enzymes
1.4.10A-A* (AO3/4) - Proteins
1.4.11Diagnostic Misconceptions - Enzyme Inhibitors
1.5Nucleic Acids
1.6ATP
1.7Water
1.8Inorganic Ions
2Cells
2.1Cell Structure
2.2Mitosis & Cancer
2.3Transport Across Cell Membrane
2.4Cell Recognition & the Immune System
2.4.1Immune System
2.4.2Phagocytosis
2.4.3T Lymphocytes
2.4.4B Lymphocytes
2.4.5Antibodies
2.4.6Primary & Secondary Response
2.4.7Vaccines
2.4.8HIV
2.4.9Ethical Issues
2.4.10End of Topic Test - Immune System
2.4.11Exam-Style Question - Immune System
2.4.12A-A* (AO3/4) - Immune System
2.4.13Diagnostic Misconceptions - Humoral vs Cellular
3Substance Exchange
3.1Surface Area to Volume Ratio
3.2Gas Exchange
3.3Digestion & Absorption
3.4Mass Transport
3.4.1Haemoglobin
3.4.2Oxygen Transport
3.4.3The Circulatory System
3.4.4The Heart
3.4.5Blood Vessels
3.4.6Cardiovascular Disease
3.4.7Heart Dissection
3.4.8Xylem
3.4.9Phloem
3.4.10Investigating Plant Transport
3.4.11End of Topic Test - Mass Transport
3.4.12A-A* (AO3/4) - Mass Transport
3.4.13Diagnostic Misconceptions - Concentration Gradient
3.4.14Diagnostic Misconceptions - Cardiac Cycle
3.4.15Diagnostic Misconceptions - Carrying Capacity
3.4.16Diagnostic Misconceptions - Translocation
4Genetic Information & Variation
4.1DNA, Genes & Chromosomes
4.2DNA & Protein Synthesis
4.3Mutations & Meiosis
4.4Genetic Diversity & Adaptation
4.5Species & Taxonomy
4.6Biodiversity Within a Community
4.7Investigating Diversity
5Energy Transfers (A2 only)
5.1Photosynthesis
5.1.1Overview of Photosynthesis
5.1.2Photoionisation of Chlorophyll
5.1.3Production of ATP & Reduced NADP
5.1.4Cyclic Photophosphorylation
5.1.5Light-Independent Reaction
5.1.6A-A* (AO3/4) - Photosynthesis Reactions
5.1.7Limiting Factors
5.1.8Photosynthesis Experiments
5.1.9End of Topic Test - Photosynthesis
5.1.10A-A* (AO3/4) - Photosynthesis
5.2Respiration
5.2.1Overview of Respiration
5.2.2Anaerobic Respiration
5.2.3A-A* (AO3/4) - Anaerobic Respiration
5.2.4The Link Reaction
5.2.5The Krebs Cycle
5.2.6Oxidative Phosphorylation
5.2.7Respiration Experiments
5.2.8End of Topic Test - Respiration
5.2.9A-A* (AO3/4) - Respiration
5.2.10Diagnostic Misconceptions - Aerobic vs Anaerobic
5.3Energy & Ecosystems
6Responding to Change (A2 only)
6.1Nervous Communication
6.2Nervous Coordination
6.3Muscle Contraction
6.4Homeostasis
6.4.1Overview of Homeostasis
6.4.2Blood Glucose Concentration
6.4.3Controlling Blood Glucose Concentration
6.4.4End of Topic Test - Blood Glucose
6.4.5Primary & Secondary Messengers
6.4.6Diabetes Mellitus
6.4.7Measuring Glucose Concentration
6.4.8Osmoregulation
6.4.9Controlling Blood Water Potential
6.4.10ADH
6.4.11End of Topic Test - Diabetes & Osmoregulation
6.4.12A-A* (AO3/4) - Homeostasis
6.4.13Diagnostic Misconceptions - Effect of ADH
7Genetics & Ecosystems (A2 only)
7.1Genetics
7.2Populations
7.3Evolution
7.3.1Variation
7.3.2Natural Selection & Evolution
7.3.3End of Topic Test - Populations & Evolution
7.3.4Types of Selection
7.3.5Types of Selection Summary
7.3.6Overview of Speciation
7.3.7Causes of Speciation
7.3.8Diversity
7.3.9End of Topic Test - Selection & Speciation
7.3.10A-A* (AO3/4) - Populations & Evolution
7.3.11Diagnostic Misconceptions - Types of Speciation
8The Control of Gene Expression (A2 only)
8.1Mutation
8.2Gene Expression
8.2.1Stem Cells
8.2.2Stem Cells in Disease
8.2.3End of Topic Test - Mutation & Gene Epression
8.2.4A-A* (AO3/4) - Mutation & Stem Cells
8.2.5Regulating Transcription
8.2.6Epigenetics
8.2.7Epigenetics & Disease
8.2.8Regulating Translation
8.2.9Experimental Data
8.2.10End of Topic Test - Transcription & Translation
8.2.11Tumours
8.2.12Correlations & Causes
8.2.13Prevention & Treatment
8.2.14End of Topic Test - Cancer
8.2.15A-A* (AO3/4) - Gene Expression & Cancer
8.3Genome Projects
Jump to other topics
1Biological Molecules
1.1Monomers & Polymers
1.2Carbohydrates
1.3Lipids
1.4Proteins
1.4.1The Peptide Chain
1.4.2Investigating Proteins
1.4.3Primary & Secondary Protein Structure
1.4.4Tertiary & Quaternary Protein Structure
1.4.5Enzymes
1.4.6Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
1.4.7Enzyme-Controlled Reactions
1.4.8End of Topic Test - Lipids & Proteins
1.4.9A-A* (AO3/4) - Enzymes
1.4.10A-A* (AO3/4) - Proteins
1.4.11Diagnostic Misconceptions - Enzyme Inhibitors
1.5Nucleic Acids
1.6ATP
1.7Water
1.8Inorganic Ions
2Cells
2.1Cell Structure
2.2Mitosis & Cancer
2.3Transport Across Cell Membrane
2.4Cell Recognition & the Immune System
2.4.1Immune System
2.4.2Phagocytosis
2.4.3T Lymphocytes
2.4.4B Lymphocytes
2.4.5Antibodies
2.4.6Primary & Secondary Response
2.4.7Vaccines
2.4.8HIV
2.4.9Ethical Issues
2.4.10End of Topic Test - Immune System
2.4.11Exam-Style Question - Immune System
2.4.12A-A* (AO3/4) - Immune System
2.4.13Diagnostic Misconceptions - Humoral vs Cellular
3Substance Exchange
3.1Surface Area to Volume Ratio
3.2Gas Exchange
3.3Digestion & Absorption
3.4Mass Transport
3.4.1Haemoglobin
3.4.2Oxygen Transport
3.4.3The Circulatory System
3.4.4The Heart
3.4.5Blood Vessels
3.4.6Cardiovascular Disease
3.4.7Heart Dissection
3.4.8Xylem
3.4.9Phloem
3.4.10Investigating Plant Transport
3.4.11End of Topic Test - Mass Transport
3.4.12A-A* (AO3/4) - Mass Transport
3.4.13Diagnostic Misconceptions - Concentration Gradient
3.4.14Diagnostic Misconceptions - Cardiac Cycle
3.4.15Diagnostic Misconceptions - Carrying Capacity
3.4.16Diagnostic Misconceptions - Translocation
4Genetic Information & Variation
4.1DNA, Genes & Chromosomes
4.2DNA & Protein Synthesis
4.3Mutations & Meiosis
4.4Genetic Diversity & Adaptation
4.5Species & Taxonomy
4.6Biodiversity Within a Community
4.7Investigating Diversity
5Energy Transfers (A2 only)
5.1Photosynthesis
5.1.1Overview of Photosynthesis
5.1.2Photoionisation of Chlorophyll
5.1.3Production of ATP & Reduced NADP
5.1.4Cyclic Photophosphorylation
5.1.5Light-Independent Reaction
5.1.6A-A* (AO3/4) - Photosynthesis Reactions
5.1.7Limiting Factors
5.1.8Photosynthesis Experiments
5.1.9End of Topic Test - Photosynthesis
5.1.10A-A* (AO3/4) - Photosynthesis
5.2Respiration
5.2.1Overview of Respiration
5.2.2Anaerobic Respiration
5.2.3A-A* (AO3/4) - Anaerobic Respiration
5.2.4The Link Reaction
5.2.5The Krebs Cycle
5.2.6Oxidative Phosphorylation
5.2.7Respiration Experiments
5.2.8End of Topic Test - Respiration
5.2.9A-A* (AO3/4) - Respiration
5.2.10Diagnostic Misconceptions - Aerobic vs Anaerobic
5.3Energy & Ecosystems
6Responding to Change (A2 only)
6.1Nervous Communication
6.2Nervous Coordination
6.3Muscle Contraction
6.4Homeostasis
6.4.1Overview of Homeostasis
6.4.2Blood Glucose Concentration
6.4.3Controlling Blood Glucose Concentration
6.4.4End of Topic Test - Blood Glucose
6.4.5Primary & Secondary Messengers
6.4.6Diabetes Mellitus
6.4.7Measuring Glucose Concentration
6.4.8Osmoregulation
6.4.9Controlling Blood Water Potential
6.4.10ADH
6.4.11End of Topic Test - Diabetes & Osmoregulation
6.4.12A-A* (AO3/4) - Homeostasis
6.4.13Diagnostic Misconceptions - Effect of ADH
7Genetics & Ecosystems (A2 only)
7.1Genetics
7.2Populations
7.3Evolution
7.3.1Variation
7.3.2Natural Selection & Evolution
7.3.3End of Topic Test - Populations & Evolution
7.3.4Types of Selection
7.3.5Types of Selection Summary
7.3.6Overview of Speciation
7.3.7Causes of Speciation
7.3.8Diversity
7.3.9End of Topic Test - Selection & Speciation
7.3.10A-A* (AO3/4) - Populations & Evolution
7.3.11Diagnostic Misconceptions - Types of Speciation
8The Control of Gene Expression (A2 only)
8.1Mutation
8.2Gene Expression
8.2.1Stem Cells
8.2.2Stem Cells in Disease
8.2.3End of Topic Test - Mutation & Gene Epression
8.2.4A-A* (AO3/4) - Mutation & Stem Cells
8.2.5Regulating Transcription
8.2.6Epigenetics
8.2.7Epigenetics & Disease
8.2.8Regulating Translation
8.2.9Experimental Data
8.2.10End of Topic Test - Transcription & Translation
8.2.11Tumours
8.2.12Correlations & Causes
8.2.13Prevention & Treatment
8.2.14End of Topic Test - Cancer
8.2.15A-A* (AO3/4) - Gene Expression & Cancer
8.3Genome Projects
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books