3.2.1
Single-Celled Organisms
Single-Celled Organisms
Single-Celled Organisms
Single-celled organisms exchange directly with their external environment.


Need for exchange
Need for exchange
- Single-celled organisms need to obtain substances from their environment to be used in processes inside the cell (e.g. oxygen for respiration).
- Waste substances also need to be removed from the cell (e.g. carbon dioxide) to avoid harming the cell.
- Substances are exchanged by all organisms for this reason.
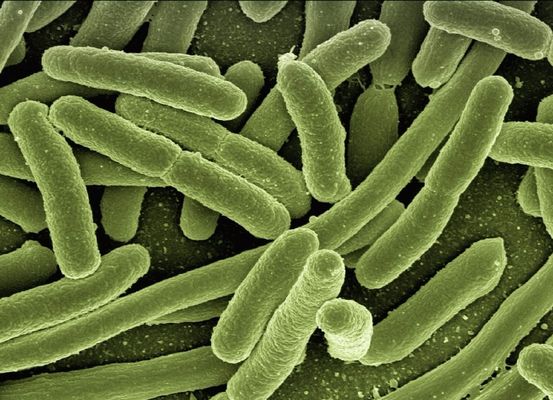

Body surface exchange
Body surface exchange
- Single-celled organisms can exchange gases and other substances using their cell membrane.
- The rate of gas exchange is increased by a larger surface area to volume ratio.
- Single-celled organisms can be adapted to increase their surface area to volume ratio (e.g. by making themselves wide, flat or with multiple folds).


Diffusion rate
Diffusion rate
- Diffusion rate is rapid for single-celled organisms because the substances only have to move across one cell-surface membrane.
1Biological Molecules
1.1Monomers & Polymers
1.2Carbohydrates
1.3Lipids
1.4Proteins
1.4.1The Peptide Chain
1.4.2Investigating Proteins
1.4.3Primary & Secondary Protein Structure
1.4.4Tertiary & Quaternary Protein Structure
1.4.5Enzymes
1.4.6Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
1.4.7Enzyme-Controlled Reactions
1.4.8End of Topic Test - Lipids & Proteins
1.4.9A-A* (AO3/4) - Enzymes
1.4.10A-A* (AO3/4) - Proteins
1.4.11Diagnostic Misconceptions - Enzyme Inhibitors
1.5Nucleic Acids
1.6ATP
1.7Water
1.8Inorganic Ions
2Cells
2.1Cell Structure
2.2Mitosis & Cancer
2.3Transport Across Cell Membrane
2.4Cell Recognition & the Immune System
2.4.1Immune System
2.4.2Phagocytosis
2.4.3T Lymphocytes
2.4.4B Lymphocytes
2.4.5Antibodies
2.4.6Primary & Secondary Response
2.4.7Vaccines
2.4.8HIV
2.4.9Ethical Issues
2.4.10End of Topic Test - Immune System
2.4.11Exam-Style Question - Immune System
2.4.12A-A* (AO3/4) - Immune System
2.4.13Diagnostic Misconceptions - Humoral vs Cellular
3Substance Exchange
3.1Surface Area to Volume Ratio
3.2Gas Exchange
3.3Digestion & Absorption
3.4Mass Transport
3.4.1Haemoglobin
3.4.2Oxygen Transport
3.4.3The Circulatory System
3.4.4The Heart
3.4.5Blood Vessels
3.4.6Cardiovascular Disease
3.4.7Heart Dissection
3.4.8Xylem
3.4.9Phloem
3.4.10Investigating Plant Transport
3.4.11End of Topic Test - Mass Transport
3.4.12A-A* (AO3/4) - Mass Transport
3.4.13Diagnostic Misconceptions - Concentration Gradient
3.4.14Diagnostic Misconceptions - Cardiac Cycle
3.4.15Diagnostic Misconceptions - Carrying Capacity
3.4.16Diagnostic Misconceptions - Translocation
4Genetic Information & Variation
4.1DNA, Genes & Chromosomes
4.2DNA & Protein Synthesis
4.3Mutations & Meiosis
4.4Genetic Diversity & Adaptation
4.5Species & Taxonomy
4.6Biodiversity Within a Community
4.7Investigating Diversity
5Energy Transfers (A2 only)
5.1Photosynthesis
5.1.1Overview of Photosynthesis
5.1.2Photoionisation of Chlorophyll
5.1.3Production of ATP & Reduced NADP
5.1.4Cyclic Photophosphorylation
5.1.5Light-Independent Reaction
5.1.6A-A* (AO3/4) - Photosynthesis Reactions
5.1.7Limiting Factors
5.1.8Photosynthesis Experiments
5.1.9End of Topic Test - Photosynthesis
5.1.10A-A* (AO3/4) - Photosynthesis
5.2Respiration
5.2.1Overview of Respiration
5.2.2Anaerobic Respiration
5.2.3A-A* (AO3/4) - Anaerobic Respiration
5.2.4The Link Reaction
5.2.5The Krebs Cycle
5.2.6Oxidative Phosphorylation
5.2.7Respiration Experiments
5.2.8End of Topic Test - Respiration
5.2.9A-A* (AO3/4) - Respiration
5.2.10Diagnostic Misconceptions - Aerobic vs Anaerobic
5.3Energy & Ecosystems
6Responding to Change (A2 only)
6.1Nervous Communication
6.2Nervous Coordination
6.3Muscle Contraction
6.4Homeostasis
6.4.1Overview of Homeostasis
6.4.2Blood Glucose Concentration
6.4.3Controlling Blood Glucose Concentration
6.4.4End of Topic Test - Blood Glucose
6.4.5Primary & Secondary Messengers
6.4.6Diabetes Mellitus
6.4.7Measuring Glucose Concentration
6.4.8Osmoregulation
6.4.9Controlling Blood Water Potential
6.4.10ADH
6.4.11End of Topic Test - Diabetes & Osmoregulation
6.4.12A-A* (AO3/4) - Homeostasis
6.4.13Diagnostic Misconceptions - Effect of ADH
7Genetics & Ecosystems (A2 only)
7.1Genetics
7.2Populations
7.3Evolution
7.3.1Variation
7.3.2Natural Selection & Evolution
7.3.3End of Topic Test - Populations & Evolution
7.3.4Types of Selection
7.3.5Types of Selection Summary
7.3.6Overview of Speciation
7.3.7Causes of Speciation
7.3.8Diversity
7.3.9End of Topic Test - Selection & Speciation
7.3.10A-A* (AO3/4) - Populations & Evolution
7.3.11Diagnostic Misconceptions - Types of Speciation
8The Control of Gene Expression (A2 only)
8.1Mutation
8.2Gene Expression
8.2.1Stem Cells
8.2.2Stem Cells in Disease
8.2.3End of Topic Test - Mutation & Gene Epression
8.2.4A-A* (AO3/4) - Mutation & Stem Cells
8.2.5Regulating Transcription
8.2.6Epigenetics
8.2.7Epigenetics & Disease
8.2.8Regulating Translation
8.2.9Experimental Data
8.2.10End of Topic Test - Transcription & Translation
8.2.11Tumours
8.2.12Correlations & Causes
8.2.13Prevention & Treatment
8.2.14End of Topic Test - Cancer
8.2.15A-A* (AO3/4) - Gene Expression & Cancer
8.3Genome Projects
Jump to other topics
1Biological Molecules
1.1Monomers & Polymers
1.2Carbohydrates
1.3Lipids
1.4Proteins
1.4.1The Peptide Chain
1.4.2Investigating Proteins
1.4.3Primary & Secondary Protein Structure
1.4.4Tertiary & Quaternary Protein Structure
1.4.5Enzymes
1.4.6Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
1.4.7Enzyme-Controlled Reactions
1.4.8End of Topic Test - Lipids & Proteins
1.4.9A-A* (AO3/4) - Enzymes
1.4.10A-A* (AO3/4) - Proteins
1.4.11Diagnostic Misconceptions - Enzyme Inhibitors
1.5Nucleic Acids
1.6ATP
1.7Water
1.8Inorganic Ions
2Cells
2.1Cell Structure
2.2Mitosis & Cancer
2.3Transport Across Cell Membrane
2.4Cell Recognition & the Immune System
2.4.1Immune System
2.4.2Phagocytosis
2.4.3T Lymphocytes
2.4.4B Lymphocytes
2.4.5Antibodies
2.4.6Primary & Secondary Response
2.4.7Vaccines
2.4.8HIV
2.4.9Ethical Issues
2.4.10End of Topic Test - Immune System
2.4.11Exam-Style Question - Immune System
2.4.12A-A* (AO3/4) - Immune System
2.4.13Diagnostic Misconceptions - Humoral vs Cellular
3Substance Exchange
3.1Surface Area to Volume Ratio
3.2Gas Exchange
3.3Digestion & Absorption
3.4Mass Transport
3.4.1Haemoglobin
3.4.2Oxygen Transport
3.4.3The Circulatory System
3.4.4The Heart
3.4.5Blood Vessels
3.4.6Cardiovascular Disease
3.4.7Heart Dissection
3.4.8Xylem
3.4.9Phloem
3.4.10Investigating Plant Transport
3.4.11End of Topic Test - Mass Transport
3.4.12A-A* (AO3/4) - Mass Transport
3.4.13Diagnostic Misconceptions - Concentration Gradient
3.4.14Diagnostic Misconceptions - Cardiac Cycle
3.4.15Diagnostic Misconceptions - Carrying Capacity
3.4.16Diagnostic Misconceptions - Translocation
4Genetic Information & Variation
4.1DNA, Genes & Chromosomes
4.2DNA & Protein Synthesis
4.3Mutations & Meiosis
4.4Genetic Diversity & Adaptation
4.5Species & Taxonomy
4.6Biodiversity Within a Community
4.7Investigating Diversity
5Energy Transfers (A2 only)
5.1Photosynthesis
5.1.1Overview of Photosynthesis
5.1.2Photoionisation of Chlorophyll
5.1.3Production of ATP & Reduced NADP
5.1.4Cyclic Photophosphorylation
5.1.5Light-Independent Reaction
5.1.6A-A* (AO3/4) - Photosynthesis Reactions
5.1.7Limiting Factors
5.1.8Photosynthesis Experiments
5.1.9End of Topic Test - Photosynthesis
5.1.10A-A* (AO3/4) - Photosynthesis
5.2Respiration
5.2.1Overview of Respiration
5.2.2Anaerobic Respiration
5.2.3A-A* (AO3/4) - Anaerobic Respiration
5.2.4The Link Reaction
5.2.5The Krebs Cycle
5.2.6Oxidative Phosphorylation
5.2.7Respiration Experiments
5.2.8End of Topic Test - Respiration
5.2.9A-A* (AO3/4) - Respiration
5.2.10Diagnostic Misconceptions - Aerobic vs Anaerobic
5.3Energy & Ecosystems
6Responding to Change (A2 only)
6.1Nervous Communication
6.2Nervous Coordination
6.3Muscle Contraction
6.4Homeostasis
6.4.1Overview of Homeostasis
6.4.2Blood Glucose Concentration
6.4.3Controlling Blood Glucose Concentration
6.4.4End of Topic Test - Blood Glucose
6.4.5Primary & Secondary Messengers
6.4.6Diabetes Mellitus
6.4.7Measuring Glucose Concentration
6.4.8Osmoregulation
6.4.9Controlling Blood Water Potential
6.4.10ADH
6.4.11End of Topic Test - Diabetes & Osmoregulation
6.4.12A-A* (AO3/4) - Homeostasis
6.4.13Diagnostic Misconceptions - Effect of ADH
7Genetics & Ecosystems (A2 only)
7.1Genetics
7.2Populations
7.3Evolution
7.3.1Variation
7.3.2Natural Selection & Evolution
7.3.3End of Topic Test - Populations & Evolution
7.3.4Types of Selection
7.3.5Types of Selection Summary
7.3.6Overview of Speciation
7.3.7Causes of Speciation
7.3.8Diversity
7.3.9End of Topic Test - Selection & Speciation
7.3.10A-A* (AO3/4) - Populations & Evolution
7.3.11Diagnostic Misconceptions - Types of Speciation
8The Control of Gene Expression (A2 only)
8.1Mutation
8.2Gene Expression
8.2.1Stem Cells
8.2.2Stem Cells in Disease
8.2.3End of Topic Test - Mutation & Gene Epression
8.2.4A-A* (AO3/4) - Mutation & Stem Cells
8.2.5Regulating Transcription
8.2.6Epigenetics
8.2.7Epigenetics & Disease
8.2.8Regulating Translation
8.2.9Experimental Data
8.2.10End of Topic Test - Transcription & Translation
8.2.11Tumours
8.2.12Correlations & Causes
8.2.13Prevention & Treatment
8.2.14End of Topic Test - Cancer
8.2.15A-A* (AO3/4) - Gene Expression & Cancer
8.3Genome Projects
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books