5.1.3
Light-Independent Reaction
The Calvin Cycle
The Calvin Cycle
The light-independent reaction (the Calvin cycle) takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast. This reaction uses ATP, reduced NADP, CO2 and ribulose bisphosphate to produce triose phosphates.
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
1) Carbon fixation
1) Carbon fixation
- When CO2 diffuses into the leaves through stomata, it combines with ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) to give an unstable 6-carbon compound.
- This is the first reaction in the Calvin cycle and it is catalysed by an enzyme, rubisco.
- The unstable 6-carbon molecule rapidly splits into two molecules of glycerate 3-phosphate (GP).
- The combination of CO2 with RuBP is described as carbon fixation.
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
2) Reduction of glycerate 3-phosphate
2) Reduction of glycerate 3-phosphate
- The two molecules of GP are then reduced to triose phosphates (TP).
- This reaction is driven by energy from two molecules of ATP and protons from two molecules of reduced NADP.
- The ATP and reduced NADP are provided by the light-dependent reaction and are recycled after they have been used.
- One out of every six TP molecules is converted into hexose sugars but most continue in the Calvin cycle.
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
3) Regeneration of RuBP
3) Regeneration of RuBP
- Five out of every six TP molecules are not converted into sugars. These are used to regenerate RuBP.
- This reaction is driven by one molecule of ATP which is then recycled in the light-dependent reaction.
- The formation of RuBP from TP allows the Calvin cycle to continue.
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
Products of the Calvin Cycle
Products of the Calvin Cycle
Triose phosphate (TP) and glycerate 3-phosphate (GP) molecules produced in the Calvin cycle are converted into useful organic substances. These are essential for plant survival.


Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates
- Hexose sugars (monomers) are produced from two molecules of triose phosphate.
- E.g. Glucose.
- Hexose sugars can be joined together to form larger carbohydrates (polymers).
- E.g. Starch, cellulose.


Lipids
Lipids
- Lipids are made from glycerol and fatty acid chains.
- Both components of lipids are synthesised from the products of the Calvin cycle:
- Triose phosphates are used in the synthesis of glycerol.
- Fatty acids are formed from glycerate 3-phosphate.
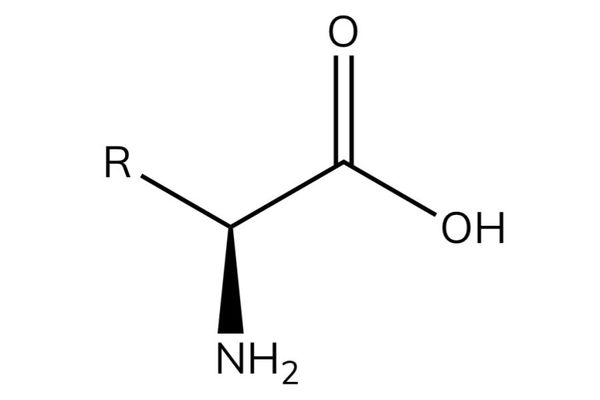

Amino acids
Amino acids
- Glycerate 3-phosphate is used in the synthesis of some amino acids.
1Biological Molecules
1.1Monomers & Polymers
1.2Carbohydrates
1.3Lipids
1.4Proteins
1.4.1The Peptide Chain
1.4.2Investigating Proteins
1.4.3Primary & Secondary Protein Structure
1.4.4Tertiary & Quaternary Protein Structure
1.4.5Enzymes
1.4.6Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
1.4.7Enzyme-Controlled Reactions
1.4.8End of Topic Test - Lipids & Proteins
1.4.9A-A* (AO3/4) - Enzymes
1.4.10A-A* (AO3/4) - Proteins
1.5Nucleic Acids
1.8Inorganic Ions
2Cells
2.1Cell Structure
2.2Mitosis & Cancer
2.3Transport Across Cell Membrane
3Substance Exchange
3.1Surface Area to Volume Ratio
3.2Gas Exchange
3.3Digestion & Absorption
4Genetic Information & Variation
4.1DNA, Genes & Chromosomes
4.2DNA & Protein Synthesis
4.3Mutations & Meiosis
4.4Genetic Diversity & Adaptation
4.5Species & Taxonomy
4.6Biodiversity Within a Community
4.7Investigating Diversity
5Energy Transfers (A2 only)
5.1Photosynthesis
5.2Respiration
5.3Energy & Ecosystems
6Responding to Change (A2 only)
6.1Nervous Communication
6.2Nervous Coordination
6.3Muscle Contraction
6.4Homeostasis
6.4.1Overview of Homeostasis
6.4.2Blood Glucose Concentration
6.4.3Controlling Blood Glucose Concentration
6.4.4End of Topic Test - Blood Glucose
6.4.5Primary & Secondary Messengers
6.4.6Diabetes Mellitus
6.4.7Measuring Glucose Concentration
6.4.8Osmoregulation
6.4.9Controlling Blood Water Potential
6.4.10ADH
6.4.11End of Topic Test - Diabetes & Osmoregulation
6.4.12A-A* (AO3/4) - Homeostasis
7Genetics & Ecosystems (A2 only)
7.1Genetics
7.2Populations
7.3Evolution
7.3.1Variation
7.3.2Natural Selection & Evolution
7.3.3End of Topic Test - Populations & Evolution
7.3.4Types of Selection
7.3.5Types of Selection Summary
7.3.6Overview of Speciation
7.3.7Causes of Speciation
7.3.8Diversity
7.3.9End of Topic Test - Selection & Speciation
7.3.10A-A* (AO3/4) - Populations & Evolution
8The Control of Gene Expression (A2 only)
8.2Gene Expression
8.2.1Stem Cells
8.2.2Stem Cells in Disease
8.2.3End of Topic Test - Mutation & Gene Epression
8.2.4A-A* (AO3/4) - Mutation & Stem Cells
8.2.5Regulating Transcription
8.2.6Epigenetics
8.2.7Epigenetics & Disease
8.2.8Regulating Translation
8.2.9Experimental Data
8.2.10End of Topic Test - Transcription & Translation
8.2.11Tumours
8.2.12Correlations & Causes
8.2.13Prevention & Treatment
8.2.14End of Topic Test - Cancer
8.2.15A-A* (AO3/4) - Gene Expression & Cancer
8.3Genome Projects
Jump to other topics
1Biological Molecules
1.1Monomers & Polymers
1.2Carbohydrates
1.3Lipids
1.4Proteins
1.4.1The Peptide Chain
1.4.2Investigating Proteins
1.4.3Primary & Secondary Protein Structure
1.4.4Tertiary & Quaternary Protein Structure
1.4.5Enzymes
1.4.6Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
1.4.7Enzyme-Controlled Reactions
1.4.8End of Topic Test - Lipids & Proteins
1.4.9A-A* (AO3/4) - Enzymes
1.4.10A-A* (AO3/4) - Proteins
1.5Nucleic Acids
1.8Inorganic Ions
2Cells
2.1Cell Structure
2.2Mitosis & Cancer
2.3Transport Across Cell Membrane
3Substance Exchange
3.1Surface Area to Volume Ratio
3.2Gas Exchange
3.3Digestion & Absorption
4Genetic Information & Variation
4.1DNA, Genes & Chromosomes
4.2DNA & Protein Synthesis
4.3Mutations & Meiosis
4.4Genetic Diversity & Adaptation
4.5Species & Taxonomy
4.6Biodiversity Within a Community
4.7Investigating Diversity
5Energy Transfers (A2 only)
5.1Photosynthesis
5.2Respiration
5.3Energy & Ecosystems
6Responding to Change (A2 only)
6.1Nervous Communication
6.2Nervous Coordination
6.3Muscle Contraction
6.4Homeostasis
6.4.1Overview of Homeostasis
6.4.2Blood Glucose Concentration
6.4.3Controlling Blood Glucose Concentration
6.4.4End of Topic Test - Blood Glucose
6.4.5Primary & Secondary Messengers
6.4.6Diabetes Mellitus
6.4.7Measuring Glucose Concentration
6.4.8Osmoregulation
6.4.9Controlling Blood Water Potential
6.4.10ADH
6.4.11End of Topic Test - Diabetes & Osmoregulation
6.4.12A-A* (AO3/4) - Homeostasis
7Genetics & Ecosystems (A2 only)
7.1Genetics
7.2Populations
7.3Evolution
7.3.1Variation
7.3.2Natural Selection & Evolution
7.3.3End of Topic Test - Populations & Evolution
7.3.4Types of Selection
7.3.5Types of Selection Summary
7.3.6Overview of Speciation
7.3.7Causes of Speciation
7.3.8Diversity
7.3.9End of Topic Test - Selection & Speciation
7.3.10A-A* (AO3/4) - Populations & Evolution
8The Control of Gene Expression (A2 only)
8.2Gene Expression
8.2.1Stem Cells
8.2.2Stem Cells in Disease
8.2.3End of Topic Test - Mutation & Gene Epression
8.2.4A-A* (AO3/4) - Mutation & Stem Cells
8.2.5Regulating Transcription
8.2.6Epigenetics
8.2.7Epigenetics & Disease
8.2.8Regulating Translation
8.2.9Experimental Data
8.2.10End of Topic Test - Transcription & Translation
8.2.11Tumours
8.2.12Correlations & Causes
8.2.13Prevention & Treatment
8.2.14End of Topic Test - Cancer
8.2.15A-A* (AO3/4) - Gene Expression & Cancer
8.3Genome Projects

Unlock your full potential with GoStudent tutoring
Affordable 1:1 tutoring from the comfort of your home
Tutors are matched to your specific learning needs
30+ school subjects covered