3.2.4
Theories of Socialisation
Structural Approaches
Structural Approaches
Theories of socialisation include structural approaches, social action approaches, structuration theory, and postmodernists approaches.


Structural approaches
Structural approaches
- Structural approaches adopt a macro-approach, in which individuals are passive victims of social forces that are beyond their control.
- Structuralists include functionalists, some feminists, and Marxists.
- Structural approaches see culture and identities as created and manipulated by the agencies of primary and secondary socialisation, making up the social structure of society.


Identity formation
Identity formation
- According to structuralism, individuals have little choice or control over their identity formation and they are compelled to conform to factors such as class and gender by various positive and negative sanctions.
- Functionalists see socialisation as a benevolent process, acting as a kind of social glue, with shared values and norms bonding people together; this integrates people into society and generates social stability.
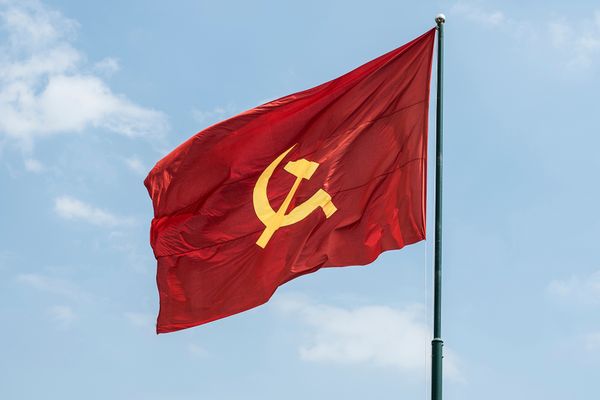


Marxists
Marxists
- Marxists see socialisation as a form of social control in unequal societies based on inequality and conflict; socialisation is, therefore, about persuading people into accepting and conforming to the ruling class ideology.

Feminists
Feminists
- Feminists emphasise how the agencies of socialisation reinforce and reproduce patriarchy, often encouraging males and females to conform to traditional gender roles.


Criticisms
Criticisms
- Individuals are seen as, what Garfinkel called ‘cultural dopes’, passively consuming and accepting norms and values handed down through socialisation.
- Structural approaches don’t recognise the existence of free will and that individuals can actively take initiatives, make choices, challenge and disobey social rules, and have a role in carving out their identities in interaction with others.
Structuration Theory and Postmodernism
Structuration Theory and Postmodernism
This is a theory proposed by Giddens, that acts as a middle way between structure and social action approaches. Postmodernists argue that identity isn’t imposed by social structures and the socialisation process.


Structuration theory
Structuration theory
- Structuration theory proposes that the structure of society and socialisation provide some predictability in social life via an understanding of basic social norms and values and a common language.
- These enable people to establish their identities and make sense of society.


Cultural frameworks
Cultural frameworks
- People do have the freedom to make choices and have opportunities to form and change their identities (as in social action approaches) but only within the cultural framework of their society.
- The identity of individuals remains reflexive, in that identity forms, develops and changes as people continually reflect, work on and re-work their identities as they go through life and interact with other individuals and agencies of socialisation.


Postmodernist approaches
Postmodernist approaches
- Postmodernist approaches include those associated with sociologists such as Bauman, Baudrillard and Lyotard.
- Postmodernists argue that identity isn’t imposed by social structures and the socialisation process.


Metanarratives
Metanarratives
- Identities once they are fixed and stable and arising from broad categories such as social class, gender, nationality and ethnicity (what Lyotard calls ‘metanarratives’) have become more fluid, unstable, fragmented and changeable.


‘Pick n mix’
‘Pick n mix’
- Due to the rise in influence of the mass media and its global reach, people are now exposed to a diversity of cultures, allowing them to ‘pick n mix’ as they choose.
- Identity becomes freely chosen according to different tastes and lifestyle choices.
1Theory & Methods
1.1Sociological Theories
1.2Sociological Methods
2Education with Methods in Context
2.1Role & Function of the Education System
2.2Educational Achievement
2.3Relationships & Processes Within Schools
3Option 1: Culture & Identity
3.1Conceptions of Culture
3.2Identity & Socialisation
3.3Social Identity
3.4Production, Consumption & Globalisation
4Option 1: Families & Households
4.1Families & Households
4.2Changing Patterns
4.3The Symmetrical Family
4.4Children & Childhood
5Option 1: Health
5.1Social Constructions
5.2Social Distribution of Healthcare
5.3Provision & Access to Healthcare
5.4Mental Health
6Option 1: Work, Poverty & Welfare
6.1Poverty & Wealth
7Option 2: Beliefs in Society
7.1Ideology, Science & Religion
7.2Religious Movements
7.3Society & Religion
8Option 2: Global Development
8.1Development, Underdevelopment & Global Inequality
8.2Globalisation & Global Organisations
8.3Aid, Trade, Industrialisation, Urbanisation
9Option 2: The Media
9.1Contemporary Media
9.2Media Representations
10Crime & Deviance
10.1Crime & Society
10.2Social Distribution of Crime
Jump to other topics
1Theory & Methods
1.1Sociological Theories
1.2Sociological Methods
2Education with Methods in Context
2.1Role & Function of the Education System
2.2Educational Achievement
2.3Relationships & Processes Within Schools
3Option 1: Culture & Identity
3.1Conceptions of Culture
3.2Identity & Socialisation
3.3Social Identity
3.4Production, Consumption & Globalisation
4Option 1: Families & Households
4.1Families & Households
4.2Changing Patterns
4.3The Symmetrical Family
4.4Children & Childhood
5Option 1: Health
5.1Social Constructions
5.2Social Distribution of Healthcare
5.3Provision & Access to Healthcare
5.4Mental Health
6Option 1: Work, Poverty & Welfare
6.1Poverty & Wealth
7Option 2: Beliefs in Society
7.1Ideology, Science & Religion
7.2Religious Movements
7.3Society & Religion
8Option 2: Global Development
8.1Development, Underdevelopment & Global Inequality
8.2Globalisation & Global Organisations
8.3Aid, Trade, Industrialisation, Urbanisation
9Option 2: The Media
9.1Contemporary Media
9.2Media Representations
10Crime & Deviance
10.1Crime & Society
10.2Social Distribution of Crime
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books

Social Action (Interpretivist/Interactionist) Approaches
Theories of socialisation include structural approaches, social action approaches, structuration theory, and postmodernists approaches.
Social action approaches
The Looking Glass self
Dramaturgy
‘The presentation of self’
Impression management
Criticisms