9.4.2
Light-Independent Reaction
After reading these notes, test your knowledge with free interactive questions on Seneca — used by over 10 million students.
The Calvin Cycle
The light-independent reaction (the Calvin cycle) takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast. This reaction uses ATP, reduced NADP, CO2 and ribulose bisphosphate to produce triose phosphates.
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
1) Carbon fixation
- When CO2 diffuses into the leaves through stomata, it combines with ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) to give an unstable 6-carbon compound.
- This is the first reaction in the Calvin cycle and it is catalysed by an enzyme, rubisco.
- The unstable 6-carbon molecule rapidly splits into two molecules of glycerate 3-phosphate (GP).
- The combination of CO2 with RuBP is described as carbon fixation.
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
2) Reduction of glycerate 3-phosphate
- The two molecules of GP are then reduced to triose phosphates (TP).
- This reaction is driven by energy from two molecules of ATP and protons from two molecules of reduced NADP.
- The ATP and reduced NADP are provided by the light-dependent reaction and are recycled after they have been used.
- One out of every six TP molecules is converted into hexose sugars but most continue in the Calvin cycle.
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
3) Regeneration of RuBP
- Five out of every six TP molecules are not converted into sugars. These are used to regenerate RuBP.
- This reaction is driven by one molecule of ATP which is then recycled in the light-dependent reaction.
- The formation of RuBP from TP allows the Calvin cycle to continue.
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
Products of the Calvin Cycle
Triose phosphate (TP) and glycerate 3-phosphate (GP) molecules produced in the Calvin cycle are converted into useful organic substances. These are essential for plant survival.

Carbohydrates
- Hexose sugars (monomers) are produced from two molecules of triose phosphate.
- E.g. Glucose.
- Hexose sugars can be joined together to form larger carbohydrates (polymers).
- E.g. Starch, cellulose.

Lipids
- Lipids are made from glycerol and fatty acid chains.
- Both components of lipids are synthesised from the products of the Calvin cycle:
- Triose phosphates are used in the synthesis of glycerol.
- Fatty acids are formed from glycerate 3-phosphate.
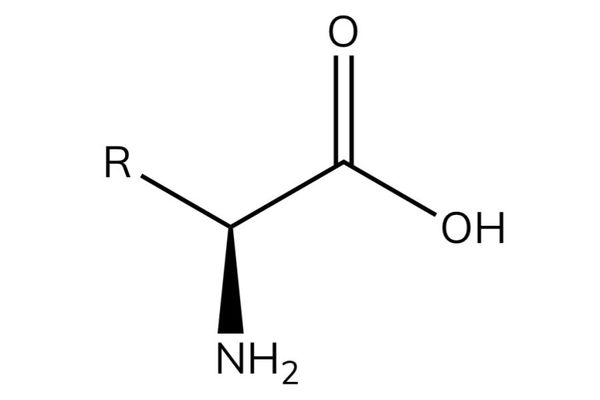
Amino acids
- Glycerate 3-phosphate is used in the synthesis of some amino acids.
1Unity & Diversity - Molecules
1.1Water
1.2DNA Structure & Replication
1.3Transcription & Gene Expression
2Unity & Diversity - Cells
2.1The Origin of Cells
2.2Introduction to Cells
2.3Ultrastructure of Cells
2.4Cell Division
2.5Structure of DNA & RNA
2.6DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation
2.7Cell Respiration
2.8Photosynthesis
2.9Viruses
3Unity & Diversity - Organisms
3.1Diversity of Organisms
3.2Evidence for Evolution
4Unity & Diversity - Ecosystems
4.1Classification
4.3Evolution & Speciation
4.3.1Evidence for Evolution - Fossils & DNA4.3.2Evidence for Evolution - Anatomy & Geography4.3.3IB Multiple Choice - Evidence for Evolution4.3.4Extended Response - DNA & Evolution4.3.5Populations4.3.6Mutations, Genetic Drift, & Gene Flow4.3.7Speciation4.3.8Rate of Speciation4.3.9Allopatric & Sympatric Speciation
4.4Conservation of Biodiversity
5Form & Function - Molecules
6Form & Function - Cells
6.1Membranes & Membrane Transport
6.2Organelles & Compartmentalization
6.3Cell Specialization
7Form & Function - Organisms
7.2Transport
7.3Muscle & Motility
8Form & Function - Ecosystems
8.1Species, Communities & Ecosytems
8.3Carbon Cycle
9Interaction & Interdependence - Molecules
9.1Enzymes
9.2Metabolism
9.3Cell Respiration
10Interaction & Interdependence - Cells
10.1Chemical Signalling
10.2Neural Signalling
10.3Adaptation to Environment
10.4Ecological Niches
11Interaction & Interdependence - Organisms
11.1Integration of Body Systems
12Interaction & Interdependence - Ecosystems
12.1Populations & Communities
12.2Transfers of Energy & Matter
13Continuity & Change - Molecules
13.1DNA Replication
13.2Protein Synthesis
14Continuity & Change - Cells
15Continuity & Change - Organisms
15.1Inheritance
15.1.1Non-Nuclear Inheritance15.1.2Linked Genes15.1.3IB Multiple Choice - Non-Mendelian Genetics15.1.4Extended Response - Inheritance15.1.5Introduction to Non-Mendelian Inheritance15.1.6Chi-Squared Test15.1.7End of Topic Quiz - Inheritance15.1.8Sex-Linked Genes15.1.9Grade 4-5 (Scientific Practices) - Inheritance
16Continuity & Change - Ecosystems
16.1Natural Selection
16.2Stability & Change
Jump to other topics
1Unity & Diversity - Molecules
1.1Water
1.2DNA Structure & Replication
1.3Transcription & Gene Expression
2Unity & Diversity - Cells
2.1The Origin of Cells
2.2Introduction to Cells
2.3Ultrastructure of Cells
2.4Cell Division
2.5Structure of DNA & RNA
2.6DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation
2.7Cell Respiration
2.8Photosynthesis
2.9Viruses
3Unity & Diversity - Organisms
3.1Diversity of Organisms
3.2Evidence for Evolution
4Unity & Diversity - Ecosystems
4.1Classification
4.3Evolution & Speciation
4.3.1Evidence for Evolution - Fossils & DNA4.3.2Evidence for Evolution - Anatomy & Geography4.3.3IB Multiple Choice - Evidence for Evolution4.3.4Extended Response - DNA & Evolution4.3.5Populations4.3.6Mutations, Genetic Drift, & Gene Flow4.3.7Speciation4.3.8Rate of Speciation4.3.9Allopatric & Sympatric Speciation
4.4Conservation of Biodiversity
5Form & Function - Molecules
6Form & Function - Cells
6.1Membranes & Membrane Transport
6.2Organelles & Compartmentalization
6.3Cell Specialization
7Form & Function - Organisms
7.2Transport
7.3Muscle & Motility
8Form & Function - Ecosystems
8.1Species, Communities & Ecosytems
8.3Carbon Cycle
9Interaction & Interdependence - Molecules
9.1Enzymes
9.2Metabolism
9.3Cell Respiration
10Interaction & Interdependence - Cells
10.1Chemical Signalling
10.2Neural Signalling
10.3Adaptation to Environment
10.4Ecological Niches
11Interaction & Interdependence - Organisms
11.1Integration of Body Systems
12Interaction & Interdependence - Ecosystems
12.1Populations & Communities
12.2Transfers of Energy & Matter
13Continuity & Change - Molecules
13.1DNA Replication
13.2Protein Synthesis
14Continuity & Change - Cells
15Continuity & Change - Organisms
15.1Inheritance
15.1.1Non-Nuclear Inheritance15.1.2Linked Genes15.1.3IB Multiple Choice - Non-Mendelian Genetics15.1.4Extended Response - Inheritance15.1.5Introduction to Non-Mendelian Inheritance15.1.6Chi-Squared Test15.1.7End of Topic Quiz - Inheritance15.1.8Sex-Linked Genes15.1.9Grade 4-5 (Scientific Practices) - Inheritance
16Continuity & Change - Ecosystems
16.1Natural Selection
16.2Stability & Change
Practice questions on Light-Independent Reaction
Can you answer these? Test yourself with free interactive practice on Seneca — used by over 10 million students.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4How many TP molecules are converted into hexose sugars?Multiple choice
- 5
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books