5.1.2
Disaccharides & Polysaccharides
After reading these notes, test your knowledge with free interactive questions on Seneca — used by over 10 million students.
Disaccharides and Polysaccharides
When two monosaccharides join via a condensation reaction, they form a disaccharide. When more than two monosaccharides join together, they form a polysaccharide chain.
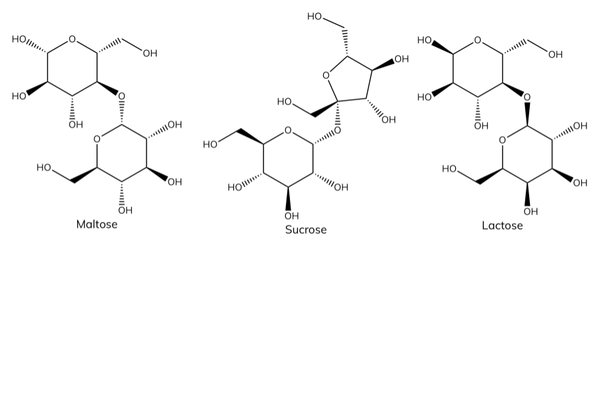
Examples of disaccharides
- Glucose + glucose → maltose.
- Glucose + fructose → sucrose.
- Glucose + galactose → lactose.
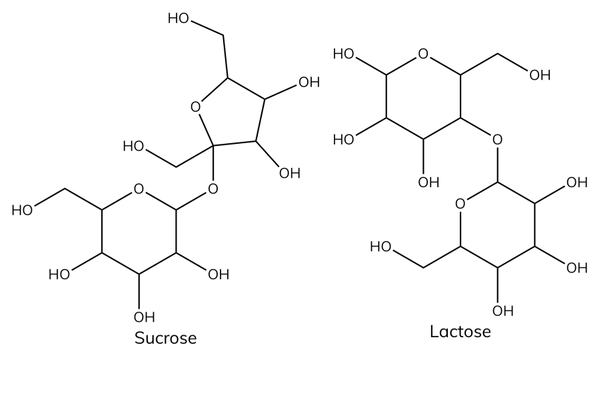
Functions of disaccharides
- Sucrose is common table sugar.
- Lactose is the sugar found in milk.
- Lactose intolerance is a common problem where the body is unable to digest lactose.
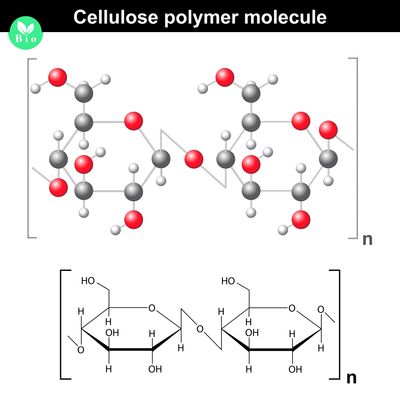
Polysaccharides
- Polysaccharides are made up of three or more monosaccharides joined together by glycosidic bonds.
- The chain may be branched or unbranched.
- The chain may contain different types of monosaccharides.
- Starch, glycogen, cellulose and chitin are examples of polysaccharides.
Benedict's Test for Sugars
Benedict’s solution (also known as Benedict's reagent or the Benedict’s test) can be used as a test for reducing and non-reducing sugars.

Reducing sugars
- All monosaccharides are reducing sugars.
- E.g. Glucose, galactose and fructose.
- Some disaccharides are reducing sugars.
- E.g. Lactose and maltose.
Test for reducing sugars
- Benedict's solution can be reduced by reducing sugars.
- Benedict's solution is a clear blue liquid that changes colour and gives a precipitate depending on how much it is reduced.
- Step 1: Place 2 ml of the substance in a boiling tube (substance must be in liquid form).
- Step 2: Add 10 drops of Benedict's solution.
- Step 3: Place in a boiling water bath for 3-5 minutes.

Results of the Benedict's test
- Blue solution → no reducing sugar.
- Green/yellow precipitate → traces of reducing sugar.
- Orange/red precipitate → moderate amounts of reducing sugar.
- Brick red precipitate → large amount of reducing sugar.
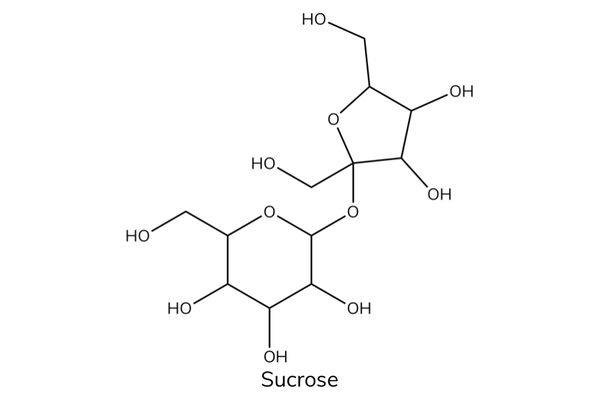
Non-reducing sugars
- Non-reducing sugars will show a negative result to the Benedict’s test. A second test is needed to determine if non-reducing sugar is present.
- Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar. It is a disaccharide made up of glucose and fructose joined by a glycosidic bond.

Test for non-reducing sugars
- Step 1: Boil in dilute HCl (to hydrolyse the non-reducing sugar).
- Step 2: Neutralise the solution by adding sodium hydrogen carbonate.
- Step 3: Repeat the Benedict’s test.
- The result will now be positive if a non-reducing sugar is present.
- If the solution remains blue, then no sugar is present.
1Unity & Diversity - Molecules
1.1Water
1.2DNA Structure & Replication
1.3Transcription & Gene Expression
2Unity & Diversity - Cells
2.1The Origin of Cells
2.2Introduction to Cells
2.3Ultrastructure of Cells
2.4Cell Division
2.5Structure of DNA & RNA
2.6DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation
2.7Cell Respiration
2.8Photosynthesis
2.9Viruses
3Unity & Diversity - Organisms
3.1Diversity of Organisms
3.2Evidence for Evolution
4Unity & Diversity - Ecosystems
4.1Classification
4.3Evolution & Speciation
4.3.1Evidence for Evolution - Fossils & DNA4.3.2Evidence for Evolution - Anatomy & Geography4.3.3IB Multiple Choice - Evidence for Evolution4.3.4Extended Response - DNA & Evolution4.3.5Populations4.3.6Mutations, Genetic Drift, & Gene Flow4.3.7Speciation4.3.8Rate of Speciation4.3.9Allopatric & Sympatric Speciation
4.4Conservation of Biodiversity
5Form & Function - Molecules
6Form & Function - Cells
6.1Membranes & Membrane Transport
6.2Organelles & Compartmentalization
6.3Cell Specialization
7Form & Function - Organisms
7.2Transport
7.3Muscle & Motility
8Form & Function - Ecosystems
8.1Species, Communities & Ecosytems
8.3Carbon Cycle
9Interaction & Interdependence - Molecules
9.1Enzymes
9.2Metabolism
9.3Cell Respiration
10Interaction & Interdependence - Cells
10.1Chemical Signalling
10.2Neural Signalling
10.3Adaptation to Environment
10.4Ecological Niches
11Interaction & Interdependence - Organisms
11.1Integration of Body Systems
12Interaction & Interdependence - Ecosystems
12.1Populations & Communities
12.2Transfers of Energy & Matter
13Continuity & Change - Molecules
13.1DNA Replication
13.2Protein Synthesis
14Continuity & Change - Cells
15Continuity & Change - Organisms
15.1Inheritance
15.1.1Non-Nuclear Inheritance15.1.2Linked Genes15.1.3IB Multiple Choice - Non-Mendelian Genetics15.1.4Extended Response - Inheritance15.1.5Introduction to Non-Mendelian Inheritance15.1.6Chi-Squared Test15.1.7End of Topic Quiz - Inheritance15.1.8Sex-Linked Genes15.1.9Grade 4-5 (Scientific Practices) - Inheritance
16Continuity & Change - Ecosystems
16.1Natural Selection
16.2Stability & Change
Jump to other topics
1Unity & Diversity - Molecules
1.1Water
1.2DNA Structure & Replication
1.3Transcription & Gene Expression
2Unity & Diversity - Cells
2.1The Origin of Cells
2.2Introduction to Cells
2.3Ultrastructure of Cells
2.4Cell Division
2.5Structure of DNA & RNA
2.6DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation
2.7Cell Respiration
2.8Photosynthesis
2.9Viruses
3Unity & Diversity - Organisms
3.1Diversity of Organisms
3.2Evidence for Evolution
4Unity & Diversity - Ecosystems
4.1Classification
4.3Evolution & Speciation
4.3.1Evidence for Evolution - Fossils & DNA4.3.2Evidence for Evolution - Anatomy & Geography4.3.3IB Multiple Choice - Evidence for Evolution4.3.4Extended Response - DNA & Evolution4.3.5Populations4.3.6Mutations, Genetic Drift, & Gene Flow4.3.7Speciation4.3.8Rate of Speciation4.3.9Allopatric & Sympatric Speciation
4.4Conservation of Biodiversity
5Form & Function - Molecules
6Form & Function - Cells
6.1Membranes & Membrane Transport
6.2Organelles & Compartmentalization
6.3Cell Specialization
7Form & Function - Organisms
7.2Transport
7.3Muscle & Motility
8Form & Function - Ecosystems
8.1Species, Communities & Ecosytems
8.3Carbon Cycle
9Interaction & Interdependence - Molecules
9.1Enzymes
9.2Metabolism
9.3Cell Respiration
10Interaction & Interdependence - Cells
10.1Chemical Signalling
10.2Neural Signalling
10.3Adaptation to Environment
10.4Ecological Niches
11Interaction & Interdependence - Organisms
11.1Integration of Body Systems
12Interaction & Interdependence - Ecosystems
12.1Populations & Communities
12.2Transfers of Energy & Matter
13Continuity & Change - Molecules
13.1DNA Replication
13.2Protein Synthesis
14Continuity & Change - Cells
15Continuity & Change - Organisms
15.1Inheritance
15.1.1Non-Nuclear Inheritance15.1.2Linked Genes15.1.3IB Multiple Choice - Non-Mendelian Genetics15.1.4Extended Response - Inheritance15.1.5Introduction to Non-Mendelian Inheritance15.1.6Chi-Squared Test15.1.7End of Topic Quiz - Inheritance15.1.8Sex-Linked Genes15.1.9Grade 4-5 (Scientific Practices) - Inheritance
16Continuity & Change - Ecosystems
16.1Natural Selection
16.2Stability & Change
Practice questions on Disaccharides & Polysaccharides
Can you answer these? Test yourself with free interactive practice on Seneca — used by over 10 million students.
- 1What are the products of the hydrolysis of sucrose?Multiple choice
- 2
- 3What can the Benedict’s test be used to test?Fill in the list
- 4Test for Non-Reducing SugarsPut in order
- 5Which of the following describes Benedict's solution?Multiple choice
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books