2.7.4
Respiration Experiments
After reading these notes, test your knowledge with free interactive questions on Seneca — used by over 10 million students.
Investigating Respiration in Single-Celled Organisms (Yeast)
Yeast respires aerobically and anaerobically. During aerobic respiration, the transport of electrons is linked to the synthesis of ATP. This experiment will measure the rate at which this takes place.
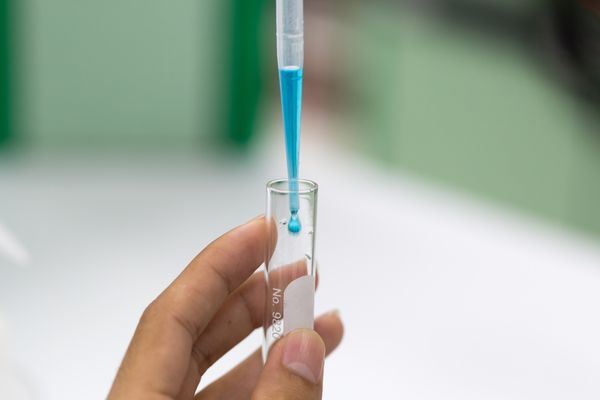
Methylene blue
- In this investigation, the electrons that are transported down the ETC will be accepted by a substance called methylene blue.
- Methylene blue is a redox indicator.
- This indicator is blue in the oxidised state and colourless in its reduced state.
- As the rate of respiration increases, methylene blue will turn colourless more quickly.

1) Mix yeast with glucose
- Use the beaker to set up a water bath at 35°C.
- Label five test tubes 1 to 5.
- Shake the yeast and glucose mixture.
- Add 2 cm3 of the yeast and glucose mixture to all five tubes.
- Place all five tubes in the water bath and leave them until the contents reach 35°C. Make sure the water bath stays at 35°C.

2) Add methylene blue
- Add 2 cm3 methylene blue to test tube 1.
- Immediately shake this tube for 10 seconds and replace the tube in the water bath. Note the time and do not shake this tube again.
- Record how long it takes for the blue colour to disappear in the tube.

3) Repeat the experiment
- Repeat steps 1 and 2 for the other four tubes.
- Repeat the whole experiment in water baths at different temperatures:
- 15°C.
- 25°C.
- 45°C.
- 55°C.
1Unity & Diversity - Molecules
1.1Water
1.2DNA Structure & Replication
1.3Transcription & Gene Expression
2Unity & Diversity - Cells
2.1The Origin of Cells
2.2Introduction to Cells
2.3Ultrastructure of Cells
2.4Cell Division
2.5Structure of DNA & RNA
2.6DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation
2.7Cell Respiration
2.8Photosynthesis
2.9Viruses
3Unity & Diversity - Organisms
3.1Diversity of Organisms
3.2Evidence for Evolution
4Unity & Diversity - Ecosystems
4.1Classification
4.3Evolution & Speciation
4.3.1Evidence for Evolution - Fossils & DNA4.3.2Evidence for Evolution - Anatomy & Geography4.3.3IB Multiple Choice - Evidence for Evolution4.3.4Extended Response - DNA & Evolution4.3.5Populations4.3.6Mutations, Genetic Drift, & Gene Flow4.3.7Speciation4.3.8Rate of Speciation4.3.9Allopatric & Sympatric Speciation
4.4Conservation of Biodiversity
5Form & Function - Molecules
6Form & Function - Cells
6.1Membranes & Membrane Transport
6.2Organelles & Compartmentalization
6.3Cell Specialization
7Form & Function - Organisms
7.2Transport
7.3Muscle & Motility
8Form & Function - Ecosystems
8.1Species, Communities & Ecosytems
8.3Carbon Cycle
9Interaction & Interdependence - Molecules
9.1Enzymes
9.2Metabolism
9.3Cell Respiration
10Interaction & Interdependence - Cells
10.1Chemical Signalling
10.2Neural Signalling
10.3Adaptation to Environment
10.4Ecological Niches
11Interaction & Interdependence - Organisms
11.1Integration of Body Systems
12Interaction & Interdependence - Ecosystems
12.1Populations & Communities
12.2Transfers of Energy & Matter
13Continuity & Change - Molecules
13.1DNA Replication
13.2Protein Synthesis
14Continuity & Change - Cells
15Continuity & Change - Organisms
15.1Inheritance
15.1.1Non-Nuclear Inheritance15.1.2Linked Genes15.1.3IB Multiple Choice - Non-Mendelian Genetics15.1.4Extended Response - Inheritance15.1.5Introduction to Non-Mendelian Inheritance15.1.6Chi-Squared Test15.1.7End of Topic Quiz - Inheritance15.1.8Sex-Linked Genes15.1.9Grade 4-5 (Scientific Practices) - Inheritance
16Continuity & Change - Ecosystems
16.1Natural Selection
16.2Stability & Change
Jump to other topics
1Unity & Diversity - Molecules
1.1Water
1.2DNA Structure & Replication
1.3Transcription & Gene Expression
2Unity & Diversity - Cells
2.1The Origin of Cells
2.2Introduction to Cells
2.3Ultrastructure of Cells
2.4Cell Division
2.5Structure of DNA & RNA
2.6DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation
2.7Cell Respiration
2.8Photosynthesis
2.9Viruses
3Unity & Diversity - Organisms
3.1Diversity of Organisms
3.2Evidence for Evolution
4Unity & Diversity - Ecosystems
4.1Classification
4.3Evolution & Speciation
4.3.1Evidence for Evolution - Fossils & DNA4.3.2Evidence for Evolution - Anatomy & Geography4.3.3IB Multiple Choice - Evidence for Evolution4.3.4Extended Response - DNA & Evolution4.3.5Populations4.3.6Mutations, Genetic Drift, & Gene Flow4.3.7Speciation4.3.8Rate of Speciation4.3.9Allopatric & Sympatric Speciation
4.4Conservation of Biodiversity
5Form & Function - Molecules
6Form & Function - Cells
6.1Membranes & Membrane Transport
6.2Organelles & Compartmentalization
6.3Cell Specialization
7Form & Function - Organisms
7.2Transport
7.3Muscle & Motility
8Form & Function - Ecosystems
8.1Species, Communities & Ecosytems
8.3Carbon Cycle
9Interaction & Interdependence - Molecules
9.1Enzymes
9.2Metabolism
9.3Cell Respiration
10Interaction & Interdependence - Cells
10.1Chemical Signalling
10.2Neural Signalling
10.3Adaptation to Environment
10.4Ecological Niches
11Interaction & Interdependence - Organisms
11.1Integration of Body Systems
12Interaction & Interdependence - Ecosystems
12.1Populations & Communities
12.2Transfers of Energy & Matter
13Continuity & Change - Molecules
13.1DNA Replication
13.2Protein Synthesis
14Continuity & Change - Cells
15Continuity & Change - Organisms
15.1Inheritance
15.1.1Non-Nuclear Inheritance15.1.2Linked Genes15.1.3IB Multiple Choice - Non-Mendelian Genetics15.1.4Extended Response - Inheritance15.1.5Introduction to Non-Mendelian Inheritance15.1.6Chi-Squared Test15.1.7End of Topic Quiz - Inheritance15.1.8Sex-Linked Genes15.1.9Grade 4-5 (Scientific Practices) - Inheritance
16Continuity & Change - Ecosystems
16.1Natural Selection
16.2Stability & Change
Practice questions on Respiration Experiments
Can you answer these? Test yourself with free interactive practice on Seneca — used by over 10 million students.
- 1
- 2
- 3Investigating Respiration Rate in YeastPut in order
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books