4.1.2
Descriptive Writing
Section B: Descriptive Writing
Section B: Descriptive Writing
A descriptive piece uses sensory detail (sight, sound, smell, taste, touch) to describe a place, person or feeling. There is no story line. Here are some tips for writing a descriptive piece:


Use figurative language
Use figurative language
- Using figurative language helps to bring descriptions to life.
- Figurative language uses figures of speech to be more effective, persuasive or impactful. Metaphors and similes are uses of figurative language.
- E.g. My bedroom is a freezer!
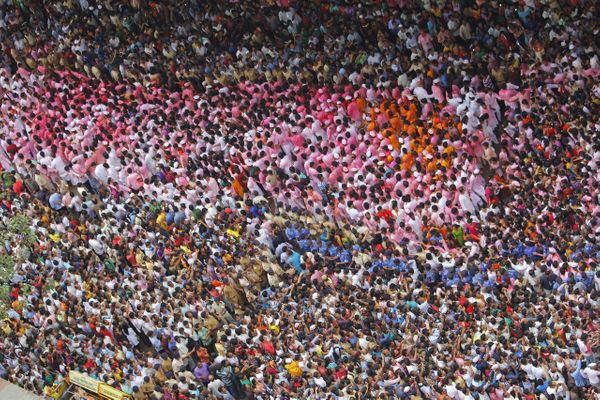
Figurative language - example
Figurative language - example
- Read this example:
- There were lots of people in the room. It was crowded. I was feeling claustrophobic. I started to panic.
- These sentences are grammatically correct, but the description is boring. Let's now look at an example using figurative language:
- The people in the room were bunched together like battery chickens on a tiny farm. Panic rushed over me like a wave crashing into shore. Claustrophobia swallowed me.
- The similes and personification in these sentences make the writing much more exciting.


Use vocabulary to create the right tone
Use vocabulary to create the right tone
- The tone of your writing is very important. The tone is the writer's feelings towards what they are describing.
- To create the right tone:
- Choose words carefully - using positive adjectives will help to create a light-hearted feel. Using negative/aggressive adjectives will help to create a foreboding atmosphere.
- Use varied sentences - using short, simple sentences will help to create suspense and quicken the pace. Using long, complex sentences will slow the pace and create a relaxed feel.
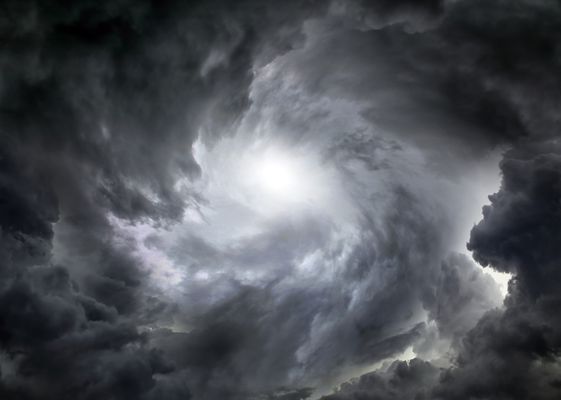


Tone - examples
Tone - examples
- The howling, raging storm smashed everything in its path.
- The aggressive adjectives help to create a negative tone. The writer wants us to think of the storm as a negative force.
- The sweet, little girl flickered her sky-blue eyes as she tossed her honey golden locks.
- The positive adjectives create a positive tone. The writer wants us to think of the girl as an attractive and likeable character.


Tone - examples
Tone - examples
- He looked. He looked again. Where was she? Where had she gone? Panic smacked Joe in the face. She was missing. Gone without a trace.
- The series of simple, short sentences help to create suspense and quicken the pace - reflecting Joe's panic.
- The golden sun stretched out his magnificent arms and spread honey rays far and wide, warming his beloved Earth and waking her creatures one and all.
- The long, complex sentence creates a relaxed feel - reflecting this lethargic start to the day.


Use a range of language devices
Use a range of language devices
- Language devices play a key role in creative writing. Using a variety of the language devices covered in the 'Key Terms' section can help you to:
- Make your writing more interesting.
- Engage the reader in your story or help them to visualise your description.
- Help you to build up the image/experience you have in your own head.
- We will recap these language devices in the 'Checklist of Techniques' section.


Good techniques
Good techniques
- Adjectives.
- Analogies.
- Metaphors and similes.
- Devices that create a visual picture in the reader's mind.
1Key Terms
2Language Techniques
2.1Language Devices
3Paper 1: Reading
4Paper 1: Writing
5Paper 2: Reading
5.1DAFORESTER
6Paper 2: Writing
6.1Structuring Your Answer
6.2Types of Writing
6.3Writing to...
6.3.1Writing to Inform
6.3.2Writing to Inform - Example
6.3.3Writing to Explain
6.3.4Writing to Explain - Example
6.3.5Writing to Persuade
6.3.6Writing to Persuade - Example
6.3.7Writing to Argue
6.3.8Writing to Argue - Example
6.3.9Writing to Persuade vs Writing to Argue
6.3.10Writing to Advise
6.3.11Writing to Advise - Example
6.3.12End of Topic Test - Writing to...
6.3.13Exam-Style Questions - Paper 2: Writing
Jump to other topics
1Key Terms
2Language Techniques
2.1Language Devices
3Paper 1: Reading
4Paper 1: Writing
5Paper 2: Reading
5.1DAFORESTER
6Paper 2: Writing
6.1Structuring Your Answer
6.2Types of Writing
6.3Writing to...
6.3.1Writing to Inform
6.3.2Writing to Inform - Example
6.3.3Writing to Explain
6.3.4Writing to Explain - Example
6.3.5Writing to Persuade
6.3.6Writing to Persuade - Example
6.3.7Writing to Argue
6.3.8Writing to Argue - Example
6.3.9Writing to Persuade vs Writing to Argue
6.3.10Writing to Advise
6.3.11Writing to Advise - Example
6.3.12End of Topic Test - Writing to...
6.3.13Exam-Style Questions - Paper 2: Writing
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books