3.3.5
Practical Graphs
Distance-Time Graphs
Distance-Time Graphs
Distance-time graphs plot the distance travelled against the time. The gradient of a distance-time graph represents the speed (velocity) and direction of movement.


Gradient
Gradient
- Steeper gradients mean faster speed and a negative gradient means the object is travelling back towards the start.
- If the graph is flat the object is stationary.


Calculating speed
Calculating speed
- To calculate the speed from a distance-time graph, work out the distance travelled and the time taken for that section and calculate:
- Speed = distance ÷ time
Velocity-Time Graphs
Velocity-Time Graphs
Velocity-time graphs plot the velocity against the time.


Velocity
Velocity
- Velocity is speed measured in a particular direction.
- Two objects travelling in opposite directions at a speed of 10km/h would have velocities of 10km/h and -10km/h.


Gradient and area
Gradient and area
- The gradient in a velocity-time graph represents acceleration.
- The area under the graph is the total distance travelled.
- When the graph is flat the velocity is constant.
- Steeper gradients mean stronger acceleration and negative slopes mean deceleration.
Conversion Graphs
Conversion Graphs
Straight line graphs can be used to convert between different units of measurement.


Drawing conversion graphs
Drawing conversion graphs
- Conversion graphs can be constructed from tables of two different units of the same measurement.
- The table above shows several distances measured in miles and the same distance measured in kilometres.


Drawing conversion graphs 2
Drawing conversion graphs 2
- To draw the conversion graph for kilometres-miles, plot these values on a graph.
- Draw a straight line from the origin that connects all of the points.
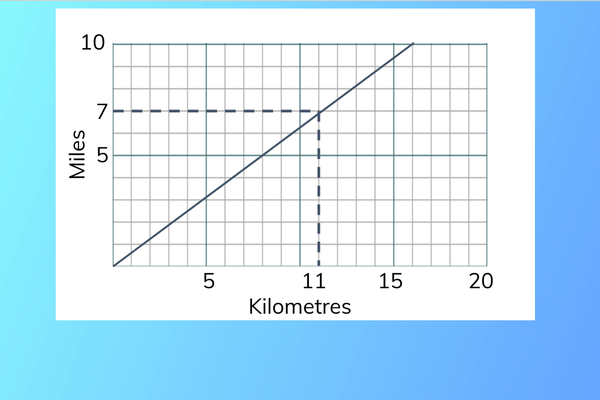

Using conversion graphs
Using conversion graphs
- To use the conversion graph, draw a line from the value you want to convert to the conversion line.
- Converting 7 miles gives approximately 11 km and vice versa.
1Numbers
1.1Integers
1.3Decimals
1.4Powers & Roots
1.5Set Language & Notation
1.6Percentages
1.7Ratio & Proportion
2Equations, Formulae & Identities
2.1Algebraic Manipulation
2.2Expressions & Formulae
2.3Linear Equations
2.4Quadratic Equations
2.5Proportion
3Sequences, Functions & Graphs
3.1Sequences
3.3Graphs
3.4Common Graphs
4Geometry
4.1Angles, Lines & Triangles
4.2Polygons
4.5Circle Properties
4.6Trigonometry & Pythagoras’ theorem
4.7Mensuration of 2D Shapes
4.83D Shapes & Volume
5Vectors & Transformation Geometry
6Statistics & Probability
6.1Statistical Measures
6.2Graphical Representation of Data
Jump to other topics
1Numbers
1.1Integers
1.3Decimals
1.4Powers & Roots
1.5Set Language & Notation
1.6Percentages
1.7Ratio & Proportion
2Equations, Formulae & Identities
2.1Algebraic Manipulation
2.2Expressions & Formulae
2.3Linear Equations
2.4Quadratic Equations
2.5Proportion
3Sequences, Functions & Graphs
3.1Sequences
3.3Graphs
3.4Common Graphs
4Geometry
4.1Angles, Lines & Triangles
4.2Polygons
4.5Circle Properties
4.6Trigonometry & Pythagoras’ theorem
4.7Mensuration of 2D Shapes
4.83D Shapes & Volume
5Vectors & Transformation Geometry
6Statistics & Probability
6.1Statistical Measures
6.2Graphical Representation of Data
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books