12.1.3
Understanding Solvents, Solutes, & Solutions
Understanding Solvents, Solutes, and Solutions
Understanding Solvents, Solutes, and Solutions
Solvents dissolve solutes to form solutions.


What is a solvent?
What is a solvent?
- A solvent is a substance that dissolves a solute.
- Solvents are usually liquids, such as water, which is a common solvent.
- Solvents create solutions by mixing with solutes.


What is a solute?
What is a solute?
- A solute is a substance dissolved in a solvent.
- Solutes can be solids, liquids, or gases.
- Salt and sugar are common solutes that dissolve in water.
- Solutes spread evenly throughout the solvent to form a solution.


What is a solution?
What is a solution?
- A solution is a mixture of one or more solutes dissolved in a solvent.
- Solutions are uniform and clear mixtures at the molecular level.
- Scientists study solutions to understand how substances combine.
- Solutions can have different concentrations depending on the solute amount.
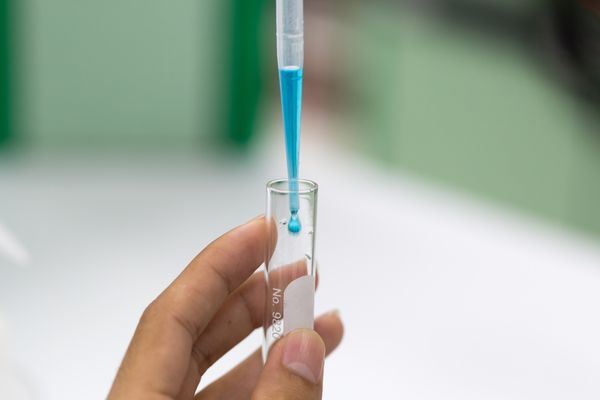

Saturated solutions
Saturated solutions
- A saturated solution contains the maximum solute dissolved at a set temperature.
- If more solute is added, it will not dissolve and may form a residue.
- Temperature affects how much solute can dissolve in a solvent.
- Saturated solutions help chemists learn about solubility limits.


Residues and filtrates
Residues and filtrates
- A residue is the solid left after evaporation, distillation, or filtration.
- Filters separate residues from filtrates in mixtures.
- A filtrate is the liquid that passes through a filter during filtering.
- These techniques help chemists purify substances and study mixtures.
1States of Matter
1.1Solids, Liquids, & Gases
2Atoms, Elements & Compounds
2.1Elements, Compounds & Mixtures
2.2Atomic Structure & the Periodic Table
2.3Isotopes
2.4Ions & Ionic Bonds
2.5Simple Molecules & Covalent Bonds
2.6Giant Covalent Structures
2.7Metallic Bonding
3Stoichometry
3.1Formulae
3.2Relative Masses of Atoms & Molecules
3.3The Mole & the Avogadro Constant
3.3.1Introducing Moles
3.3.2Amounts of Substances
3.3.3Moles & Equations
3.3.4Calculations Involving Gases
3.3.5Calculating Stoichiometric Reacting Masses
3.3.6Calculating the Moles of Solute
3.3.7Calculating Empirical Formula
3.3.8Chemical Equations
3.3.9Percentage Yield
3.3.10Calculating Yield
3.3.11Percentage Purity
4Electrochemistry
4.1Electrolysis
4.1.1Electrolytic Process
4.1.2Electrolysis Examples
4.1.3Electrolysis of a Binary Compound in Molten State
4.1.4Electroplating
4.1.5Transfer of Charge During Electrolysis
4.1.6Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions
4.1.7Electrolysis of Copper Sulfate
4.1.8Electrolysis of Halide Compounds
4.1.9Half-Equations
4.1.10Combustion of Hydrocarbons
4.2Hydrogen–Oxygen Fuel Cells
5Chemical Energetics
6Chemical Reactions
6.1Physical & Chemical Changes
6.2Rate of Reaction
6.3Reversible Reactions & Equilibrium
6.3.1Reversible Reactions
6.3.2Conditions & Equilibrium
6.3.3Dynamic Equilibrium
6.3.4Changing Conditions - Heat & Water Effects
6.3.5Factors Affecting Equilibria - Temperature
6.3.6Factors Affecting Equilibria - Pressure
6.3.7Factors Affecting Equilibria - Concentration
6.3.8The Haber Process
6.3.9The Haber Process Equation
7Acids, Bases & Salts
7.1The Characteristic Properties of Acids & Bases
7.1.1Acids & Alkali
7.1.2Reactions of Metals with Acids
7.1.3Reactions of Bases with Acids
7.1.4Reactions of Carbonates with Acids
7.1.5Identifying Acids
7.1.6Properties & Effects of Acids
7.1.7Properties of Bases - Reactions with Acids & Salts
7.1.8Properties of Alkalis & Indicators
7.1.9Strong vs Weak Acids
7.1.10Strong vs Weak Bases
7.1.11Understanding Universal Indicator Paper
7.1.12Acids, Bases & the Neutralisation Reaction
8The Periodic Table
8.1Arrangement of Elements
8.2Group I Properties
8.3Group VII Properties
8.4Transition Elements
8.5Noble Gases
9Metals
9.1Properties of Metals
9.2Uses of Metals
9.3Alloys & Their Properties
9.4Reactivity Series
9.5Corrosion of Metals
9.6Extraction of Metals
10Chemistry of the Environment
10.1Water
10.2Fertilisers
11Organic Chemistry
11.1Formulae, Functional Groups & Terminology
11.2Naming Organic Compounds
11.3Fuels
11.4Alkanes
11.5Alkenes
11.6Alcohols
11.7Carboxylic Acids
11.8Polymers
11.8.1Polymers
11.8.2Problems With Polymers
11.8.3Polymers & Plastics
11.8.4Problems with Plastics
11.8.5Condensation Polymerisation
11.8.6Condensation Polymerisation Examples
11.8.7Addition Polymerisation
11.8.8Addition Polymerisation Examples
11.8.9Structure of Polymers
11.8.10Natural Polyamides - Proteins & Amino Acids
12Experimental Techniques & Chemical Analysis
12.1Experimental Design
12.2Acid-base Titrations
12.3Chromatography
12.4Separation & Purification
12.5Identification of Ions & Gases
12.5.1Testing Aqueous Cations 1
12.5.2Testing Aqueous Cations 2
12.5.3Testing Cations - Flame Tests
12.5.4Testing Cations
12.5.5Testing for Aqueous Cations
12.5.6Testing Anions - Sulfates
12.5.7Testing Anions - Nitrates
12.5.8Testing Gases - Hydrogen
12.5.9Testing Gases - Oxygen
12.5.10Testing Gases - Carbon Dioxide
12.5.11Testing Gases - Chlorine
12.5.12Identifying Gases
Jump to other topics
1States of Matter
1.1Solids, Liquids, & Gases
2Atoms, Elements & Compounds
2.1Elements, Compounds & Mixtures
2.2Atomic Structure & the Periodic Table
2.3Isotopes
2.4Ions & Ionic Bonds
2.5Simple Molecules & Covalent Bonds
2.6Giant Covalent Structures
2.7Metallic Bonding
3Stoichometry
3.1Formulae
3.2Relative Masses of Atoms & Molecules
3.3The Mole & the Avogadro Constant
3.3.1Introducing Moles
3.3.2Amounts of Substances
3.3.3Moles & Equations
3.3.4Calculations Involving Gases
3.3.5Calculating Stoichiometric Reacting Masses
3.3.6Calculating the Moles of Solute
3.3.7Calculating Empirical Formula
3.3.8Chemical Equations
3.3.9Percentage Yield
3.3.10Calculating Yield
3.3.11Percentage Purity
4Electrochemistry
4.1Electrolysis
4.1.1Electrolytic Process
4.1.2Electrolysis Examples
4.1.3Electrolysis of a Binary Compound in Molten State
4.1.4Electroplating
4.1.5Transfer of Charge During Electrolysis
4.1.6Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions
4.1.7Electrolysis of Copper Sulfate
4.1.8Electrolysis of Halide Compounds
4.1.9Half-Equations
4.1.10Combustion of Hydrocarbons
4.2Hydrogen–Oxygen Fuel Cells
5Chemical Energetics
6Chemical Reactions
6.1Physical & Chemical Changes
6.2Rate of Reaction
6.3Reversible Reactions & Equilibrium
6.3.1Reversible Reactions
6.3.2Conditions & Equilibrium
6.3.3Dynamic Equilibrium
6.3.4Changing Conditions - Heat & Water Effects
6.3.5Factors Affecting Equilibria - Temperature
6.3.6Factors Affecting Equilibria - Pressure
6.3.7Factors Affecting Equilibria - Concentration
6.3.8The Haber Process
6.3.9The Haber Process Equation
7Acids, Bases & Salts
7.1The Characteristic Properties of Acids & Bases
7.1.1Acids & Alkali
7.1.2Reactions of Metals with Acids
7.1.3Reactions of Bases with Acids
7.1.4Reactions of Carbonates with Acids
7.1.5Identifying Acids
7.1.6Properties & Effects of Acids
7.1.7Properties of Bases - Reactions with Acids & Salts
7.1.8Properties of Alkalis & Indicators
7.1.9Strong vs Weak Acids
7.1.10Strong vs Weak Bases
7.1.11Understanding Universal Indicator Paper
7.1.12Acids, Bases & the Neutralisation Reaction
8The Periodic Table
8.1Arrangement of Elements
8.2Group I Properties
8.3Group VII Properties
8.4Transition Elements
8.5Noble Gases
9Metals
9.1Properties of Metals
9.2Uses of Metals
9.3Alloys & Their Properties
9.4Reactivity Series
9.5Corrosion of Metals
9.6Extraction of Metals
10Chemistry of the Environment
10.1Water
10.2Fertilisers
11Organic Chemistry
11.1Formulae, Functional Groups & Terminology
11.2Naming Organic Compounds
11.3Fuels
11.4Alkanes
11.5Alkenes
11.6Alcohols
11.7Carboxylic Acids
11.8Polymers
11.8.1Polymers
11.8.2Problems With Polymers
11.8.3Polymers & Plastics
11.8.4Problems with Plastics
11.8.5Condensation Polymerisation
11.8.6Condensation Polymerisation Examples
11.8.7Addition Polymerisation
11.8.8Addition Polymerisation Examples
11.8.9Structure of Polymers
11.8.10Natural Polyamides - Proteins & Amino Acids
12Experimental Techniques & Chemical Analysis
12.1Experimental Design
12.2Acid-base Titrations
12.3Chromatography
12.4Separation & Purification
12.5Identification of Ions & Gases
12.5.1Testing Aqueous Cations 1
12.5.2Testing Aqueous Cations 2
12.5.3Testing Cations - Flame Tests
12.5.4Testing Cations
12.5.5Testing for Aqueous Cations
12.5.6Testing Anions - Sulfates
12.5.7Testing Anions - Nitrates
12.5.8Testing Gases - Hydrogen
12.5.9Testing Gases - Oxygen
12.5.10Testing Gases - Carbon Dioxide
12.5.11Testing Gases - Chlorine
12.5.12Identifying Gases
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books