3.7.5
Amino Acids
Amino Acids
Amino Acids
There are about 20 naturally-occurring amino acids in animal cells.
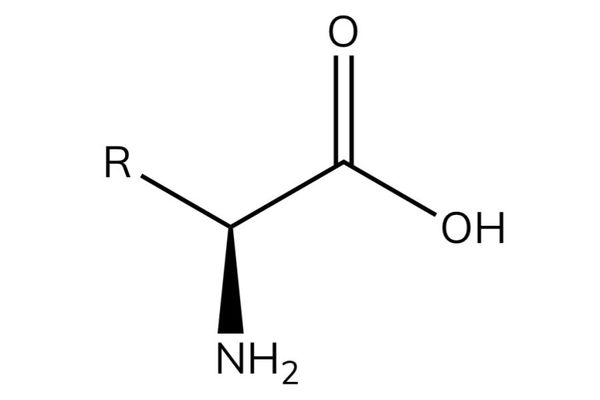

Amino acids
Amino acids
- Amino acids have the general formula RCH(NH2)COOH.
- Amino acids contain an acidic group (carboxylic acid) and a basic group (amine) in the same molecule.
- The -NH2 group is on the carbon next to the -COOH group and so they are known as α-amino acids.


Acid and base behaviour
Acid and base behaviour
- The -COOH group is acidic and can react with bases by donating a proton (H+).
- The -NH2 group is basic and can react with acids by accepting a proton (H+).
- Amino acids are amphoteric because they contain both acidic and basic groups in the same molecule.


Side chain
Side chain
- An amino acid contains an -R group which is a side chain.
- This is different for different amino acids.
- E.g. Alanine has an -R group of -CH3.
Amino Acids as an Acid and Base
Amino Acids as an Acid and Base
Amino acids have the ability to behave as an acid or a base.
Acidic and basic groups
Acidic and basic groups
- In an amino acid:
- The amine acts as a basic group.
- The carboxylic acid acts as an acidic group.
Zwitterions 1
Zwitterions 1
- There is internal movement of an H+ from the carboxylic acid group and onto the amine group to create a zwitterion.
- The resulting zwitterion has both negative -COO- and positive -NH3+ groups.
Zwitterions 2
Zwitterions 2
- Zwitterions exist in solids and in solution
- A zwitterion has no overall charge but parts of the molecule are positively and negatively charged.
1Physical Chemistry
1.1Atoms, Molecules & Stoichiometry
1.2Atomic Structure
1.2.1Fundamental Particles
1.2.2Isotopes & Mass Number
1.2.3Electron Shells, Sub-Shells & Orbitals
1.2.4Electron Configuration
1.2.5Ionisation Energy
1.2.6Factors Affecting Ionisation Energies
1.2.7Trends of Ionisation
1.2.8Specific Impacts on Ionisation Energies
1.2.9Electron Affinity
1.2.10End of Topic Test - Atomic Structure
1.2.11A-A* (AO2/3) - Atomic Structure
1.3Chemical Bonding
1.3.1Ionic Bonding
1.3.2Covalent & Dative Bonding
1.3.3Shapes of Molecules
1.3.4Intermolecular Forces
1.3.5Intermolecular Forces 2
1.3.6Electronegativity
1.3.7Bond Length, Bond Energy, & Bond Polarity
1.3.8Metallic Bonding
1.3.9Physical Properties
1.3.10End of Topic Test - Bonding
1.3.11A-A* (AO2/3) - Bonding
1.4States of Matter
1.5Chemical Energetics
1.6Electrochemistry
1.7Equilibria
1.7.1Dynamic Equilibrium & Le Chatelier
1.7.2Kc
1.7.3Kp
1.7.4pH
1.7.5The Ionic Product of Water
1.7.6Weak Acids & Bases
1.7.7Introduction to Solubility Equilibria
1.7.8Solubility Equilibria Calculations
1.7.9Free Energy of Dissolution
1.7.10pH and Solubility
1.7.11Common-Ion Effect
1.7.12End of Topic Test - Kp & Electrochemistry
1.7.13A-A* (AO2/3) - Electrochemical Cells
1.8Partition Coefficient
1.9Reaction Kinetics
1.9.1Collision Theory
1.9.2Orders, Rate Constants & Equations
1.9.3Rate Graphs
1.9.4Rate Determining Step
1.9.5Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution
1.9.6Catalysts
1.9.7Homogeneous Catalysts
1.9.8Heterogeneous Catalysts
1.9.9End of Topic Test - Kinetics
1.9.10End of Topic Test - Rate Equations
1.9.11A-A* (AO2/3) - Rate Equations
2Inorganic Chemistry
2.1The Periodic Table
2.2Group 2
2.3Group 17
2.4Transition Metals
3Organic Chemistry & Analysis
3.1Introduction to Organic Chemistry
3.2Hydrocarbons
3.2.1Fractional Distillation
3.2.2Cracking
3.2.3Combustion
3.2.4Chlorination
3.2.5End of Topic Test - Alkanes
3.2.6Introduction to Alkenes
3.2.7Reactions of Alkenes
3.2.8Polymerisation Reactions
3.2.9End of Topic Test - Alkenes
3.2.10Arenes
3.2.11Evidence for Structure of Arenes
3.2.12Reactions of Benzene
3.2.13End of Topic Test -Arenes
3.3Halogen Derivatives
3.4Hydroxy Compounds
3.5Carbonyl Compounds
3.6Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives
3.7Nitrogen Compounds
3.8Polymerisation
3.9Analytical Techniques
3.9.1Chromatography
3.9.2High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
3.9.3Gas Chromatography
3.9.4IR Spectroscopy
3.9.5Uses of IR Spectroscopy
3.9.6Mass Spectrometry
3.9.7Mass Spectrometry Analysis
3.9.8Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
3.9.9Carbon-13 NMR
3.9.10Proton NMR I
3.9.11Proton NMR II
3.9.12End of Topic Test - Analytical Techniques
3.9.13A-A* (AO2/3) - Analytical Techniques
Jump to other topics
1Physical Chemistry
1.1Atoms, Molecules & Stoichiometry
1.2Atomic Structure
1.2.1Fundamental Particles
1.2.2Isotopes & Mass Number
1.2.3Electron Shells, Sub-Shells & Orbitals
1.2.4Electron Configuration
1.2.5Ionisation Energy
1.2.6Factors Affecting Ionisation Energies
1.2.7Trends of Ionisation
1.2.8Specific Impacts on Ionisation Energies
1.2.9Electron Affinity
1.2.10End of Topic Test - Atomic Structure
1.2.11A-A* (AO2/3) - Atomic Structure
1.3Chemical Bonding
1.3.1Ionic Bonding
1.3.2Covalent & Dative Bonding
1.3.3Shapes of Molecules
1.3.4Intermolecular Forces
1.3.5Intermolecular Forces 2
1.3.6Electronegativity
1.3.7Bond Length, Bond Energy, & Bond Polarity
1.3.8Metallic Bonding
1.3.9Physical Properties
1.3.10End of Topic Test - Bonding
1.3.11A-A* (AO2/3) - Bonding
1.4States of Matter
1.5Chemical Energetics
1.6Electrochemistry
1.7Equilibria
1.7.1Dynamic Equilibrium & Le Chatelier
1.7.2Kc
1.7.3Kp
1.7.4pH
1.7.5The Ionic Product of Water
1.7.6Weak Acids & Bases
1.7.7Introduction to Solubility Equilibria
1.7.8Solubility Equilibria Calculations
1.7.9Free Energy of Dissolution
1.7.10pH and Solubility
1.7.11Common-Ion Effect
1.7.12End of Topic Test - Kp & Electrochemistry
1.7.13A-A* (AO2/3) - Electrochemical Cells
1.8Partition Coefficient
1.9Reaction Kinetics
1.9.1Collision Theory
1.9.2Orders, Rate Constants & Equations
1.9.3Rate Graphs
1.9.4Rate Determining Step
1.9.5Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution
1.9.6Catalysts
1.9.7Homogeneous Catalysts
1.9.8Heterogeneous Catalysts
1.9.9End of Topic Test - Kinetics
1.9.10End of Topic Test - Rate Equations
1.9.11A-A* (AO2/3) - Rate Equations
2Inorganic Chemistry
2.1The Periodic Table
2.2Group 2
2.3Group 17
2.4Transition Metals
3Organic Chemistry & Analysis
3.1Introduction to Organic Chemistry
3.2Hydrocarbons
3.2.1Fractional Distillation
3.2.2Cracking
3.2.3Combustion
3.2.4Chlorination
3.2.5End of Topic Test - Alkanes
3.2.6Introduction to Alkenes
3.2.7Reactions of Alkenes
3.2.8Polymerisation Reactions
3.2.9End of Topic Test - Alkenes
3.2.10Arenes
3.2.11Evidence for Structure of Arenes
3.2.12Reactions of Benzene
3.2.13End of Topic Test -Arenes
3.3Halogen Derivatives
3.4Hydroxy Compounds
3.5Carbonyl Compounds
3.6Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives
3.7Nitrogen Compounds
3.8Polymerisation
3.9Analytical Techniques
3.9.1Chromatography
3.9.2High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
3.9.3Gas Chromatography
3.9.4IR Spectroscopy
3.9.5Uses of IR Spectroscopy
3.9.6Mass Spectrometry
3.9.7Mass Spectrometry Analysis
3.9.8Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
3.9.9Carbon-13 NMR
3.9.10Proton NMR I
3.9.11Proton NMR II
3.9.12End of Topic Test - Analytical Techniques
3.9.13A-A* (AO2/3) - Analytical Techniques
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books