3.1.1
Enzyme Action
Function of Enzymes
Function of Enzymes
Metabolism is the different processes that take place in living organisms to allow them to survive. Enzymes are the proteins that catalyse (speed up) these reactions, they are biological catalysts.


Catalysts
Catalysts
- Enzymes are called biological catalysts because they speed up reactions in living organisms.
- E.g. Rubisco in plant cells catalyses the fixation of CO2 in photosynthesis.
- E.g. Amylase in your saliva catalyses the break down of starch to sugars when you eat.


Effect on the organism
Effect on the organism
- Enzymes speed up reactions that affect the organism on the cellular and individual level.
- E.g. Enzymes catalyse photosynthesis that takes place in cells. The products of photosynthesis (fixed carbon) are used around the plant on the organismal level to grow roots and shoots.


Structure and function
Structure and function
- Enzymes speed up reactions that affect both structure and function.
- E.g. Enzymes catalyse the production of collagen, a structural protein in bones.
- E.g. Enzymes catalyse respiration, the reaction that produces ATP.
Models of Enzyme Action
Models of Enzyme Action
Models of enzyme action have changed over time. For many years, it was thought that enzymes worked in a lock and key manner. The induced fit model is now more widely accepted.
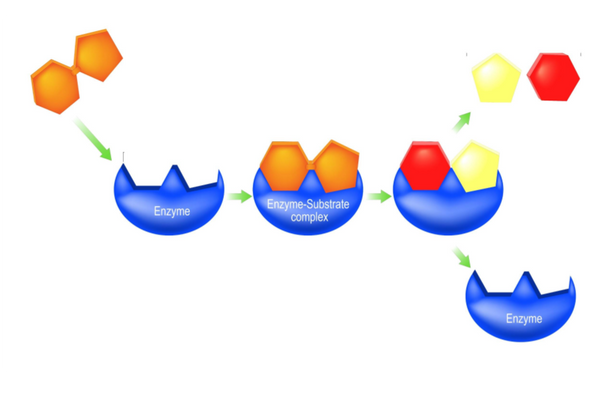

The lock and key model
The lock and key model
- The lock and key model was originally used to explain enzyme action.
- The model proposes that the enzyme and substrate fit together perfectly.
- The substrate is a key fitting into a lock (the enzyme).
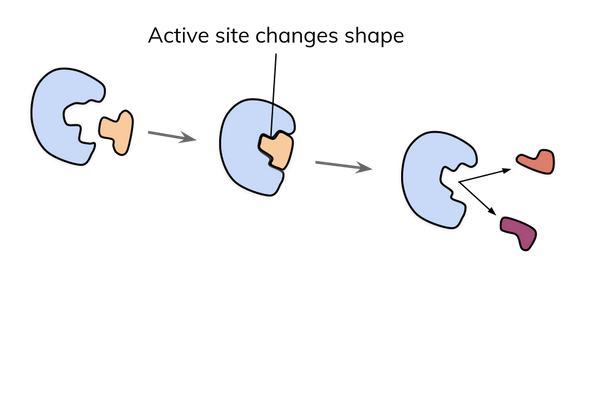

The induced fit model
The induced fit model
- The induced fit model suggests there is a more dynamic interaction between enzyme and substrate.
- The model states that as an enzyme and substrate come together, their interaction causes a small shift in the enzyme’s structure.
- The shift means that the enzyme and substrate can bind to form an enzyme-substrate complex and catalyse a reaction.
- This model is now more widely accepted.
Enzyme-Substrate Complexes
Enzyme-Substrate Complexes
Enzymes bind with substrates to form an enzyme-substrate complex in a specific fashion. The specificity of enzymes is determined by two things:


Active site
Active site
- Every enzyme only catalyses one specific reaction.
- Every enzyme has a specific active site that is complementary to the specific substrate.
- This jigsaw puzzle-like match between an enzyme and its substrates is what makes enzymes highly specific.
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
Environmental factors
Environmental factors
- The 3D, tertiary structure of the polypeptide chain determines the shape of the active site.
- Environmental changes can change the tertiary structure of the active site and can stop the enzyme from working properly.
- This is called a denatured enzyme.
1Cell Structure
1.1Cell Structure
1.1.1Studying Cells - Microscopes
1.1.2Introduction to Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.3Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells
1.1.4Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 2
1.1.5Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 3
1.1.6Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.7Viruses
1.1.8End of Topic Test - Cell Structure
1.1.9Exam-Style Question - Microscopes
1.1.10A-A* (AO2/3) - Cell Structure
2Biological Molecules
2.1Testing for Biological Modules
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
3Enzymes
4Cell Membranes & Transport
4.1Biological Membranes
5The Mitotic Cell Cycle
6Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis
6.1Nucleic Acids
7Transport in Plants
8Transport in Mammals
8.1Circulatory System
8.2Transport of Oxygen & Carbon Dioxide
9Gas Exchange
9.1Gas Exchange System
10Infectious Diseases
10.1Infectious Diseases
10.2Antibiotics
11Immunity
12Energy & Respiration (A2 Only)
13Photosynthesis (A2 Only)
14Homeostasis (A2 Only)
14.1Homeostasis
14.2The Kidney
14.3Cell Signalling
14.4Blood Glucose Concentration
14.5Homeostasis in Plants
15Control & Coordination (A2 Only)
15.1Control & Coordination in Mammals
15.1.1Neurones
15.1.2Receptors
15.1.3Taste
15.1.4Reflexes
15.1.5Action Potentials
15.1.6Saltatory Conduction
15.1.7Synapses
15.1.8Cholinergic Synnapses
15.1.9Neuromuscular Junction
15.1.10Skeletal Muscle
15.1.11Sliding Filament Theory Contraction
15.1.12Sliding Filament Theory Contraction 2
15.1.13Menstruation
15.1.14Contraceptive Pill
15.2Control & Co-Ordination in Plants
16Inherited Change (A2 Only)
16.1Passage of Information to Offspring
16.2Genes & Phenotype
17Selection & Evolution (A2 Only)
17.2Natural & Artificial Selection
18Classification & Conservation (A2 Only)
18.1Biodiversity
18.2Classification
19Genetic Technology (A2 Only)
19.1Manipulating Genomes
19.2Genetic Technology Applied to Medicine
19.3Genetically Modified Organisms in Agriculture
Jump to other topics
1Cell Structure
1.1Cell Structure
1.1.1Studying Cells - Microscopes
1.1.2Introduction to Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.3Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells
1.1.4Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 2
1.1.5Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 3
1.1.6Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.7Viruses
1.1.8End of Topic Test - Cell Structure
1.1.9Exam-Style Question - Microscopes
1.1.10A-A* (AO2/3) - Cell Structure
2Biological Molecules
2.1Testing for Biological Modules
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
3Enzymes
4Cell Membranes & Transport
4.1Biological Membranes
5The Mitotic Cell Cycle
6Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis
6.1Nucleic Acids
7Transport in Plants
8Transport in Mammals
8.1Circulatory System
8.2Transport of Oxygen & Carbon Dioxide
9Gas Exchange
9.1Gas Exchange System
10Infectious Diseases
10.1Infectious Diseases
10.2Antibiotics
11Immunity
12Energy & Respiration (A2 Only)
13Photosynthesis (A2 Only)
14Homeostasis (A2 Only)
14.1Homeostasis
14.2The Kidney
14.3Cell Signalling
14.4Blood Glucose Concentration
14.5Homeostasis in Plants
15Control & Coordination (A2 Only)
15.1Control & Coordination in Mammals
15.1.1Neurones
15.1.2Receptors
15.1.3Taste
15.1.4Reflexes
15.1.5Action Potentials
15.1.6Saltatory Conduction
15.1.7Synapses
15.1.8Cholinergic Synnapses
15.1.9Neuromuscular Junction
15.1.10Skeletal Muscle
15.1.11Sliding Filament Theory Contraction
15.1.12Sliding Filament Theory Contraction 2
15.1.13Menstruation
15.1.14Contraceptive Pill
15.2Control & Co-Ordination in Plants
16Inherited Change (A2 Only)
16.1Passage of Information to Offspring
16.2Genes & Phenotype
17Selection & Evolution (A2 Only)
17.2Natural & Artificial Selection
18Classification & Conservation (A2 Only)
18.1Biodiversity
18.2Classification
19Genetic Technology (A2 Only)
19.1Manipulating Genomes
19.2Genetic Technology Applied to Medicine
19.3Genetically Modified Organisms in Agriculture
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books