13.1.3
Light-Independent Reactions
The Calvin Cycle
The Calvin Cycle
The light-independent reaction (the Calvin cycle) takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast. This reaction uses ATP, reduced NADP, CO2 and ribulose bisphosphate to produce triose phosphates.
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
1) Carbon fixation
1) Carbon fixation
- When CO2 diffuses into the leaves through stomata, it combines with ribulose bisposphate (RuBP) to give an unstable 6-carbon compound.
- This is the first reaction in the Calvin cycle and it is catalysed by an enzyme, RuBisCO.
- The unstable 6-carbon molecule rapidly splits into two molecules of glycerate 3-phosphate (GP).
- The combination of CO2 with RuBP is described as carbon fixation.
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
2) Reduction of glycerate 3-phosphate
2) Reduction of glycerate 3-phosphate
- The two molecules of GP are then reduced to triose phosphates (TP).
- This reaction is driven by energy from two molecules of ATP and protons from two molecules of reduced NADP.
- The ATP and reduced NADP are provided by the light-dependent reaction and are recycled after they have been used.
- One out of every six TP molecules is converted into hexose sugars but most continue in the Calvin cycle.
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
3) Regeneration of RuBP
3) Regeneration of RuBP
- Five out of every six TP molecules are not converted into sugars. These are used to regenerate RuBP.
- This reaction is driven by one molecule of ATP which is then recycled in the light-dependent reaction.
- The formation of RuBP from TP allows the Calvin cycle to continue.
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
Products of the Calvin Cycle
Products of the Calvin Cycle
Triose phosphate (TP) and glycerate 3-phosphate (GP) molecules produced in the Calvin cycle are converted into useful organic substances. These are essential for plant survival.


Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates
- Hexose sugars (monomers) are produced from two molecules of triose phosphate.
- E.g. Glucose.
- Hexose sugars can be joined together to form larger carbohydrates (polymers).
- E.g. Starch, cellulose.


Lipids
Lipids
- Lipids are made from glycerol and fatty acid chains.
- Both components of lipids are synthesised from the products of the Calvin cycle:
- Triose phosphates are used in the synthesis of glycerol.
- Fatty acids are formed from glycerate 3-phosphate.
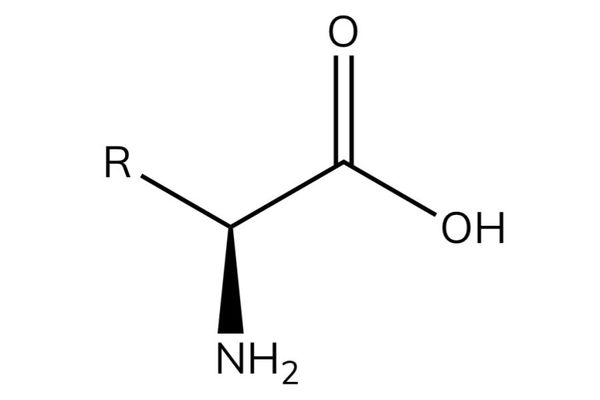

Amino acids
Amino acids
- Glycerate 3-phosphate is used in the synthesis of some amino acids.
1Cell Structure
1.1Cell Structure
1.1.1Studying Cells - Microscopes
1.1.2Introduction to Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.3Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells
1.1.4Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 2
1.1.5Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 3
1.1.6Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.7Viruses
1.1.8End of Topic Test - Cell Structure
1.1.9Exam-Style Question - Microscopes
1.1.10A-A* (AO2/3) - Cell Structure
2Biological Molecules
2.1Testing for Biological Modules
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
3Enzymes
4Cell Membranes & Transport
4.1Biological Membranes
5The Mitotic Cell Cycle
6Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis
6.1Nucleic Acids
7Transport in Plants
8Transport in Mammals
8.1Circulatory System
8.2Transport of Oxygen & Carbon Dioxide
9Gas Exchange
9.1Gas Exchange System
10Infectious Diseases
10.1Infectious Diseases
10.2Antibiotics
11Immunity
12Energy & Respiration (A2 Only)
13Photosynthesis (A2 Only)
14Homeostasis (A2 Only)
14.1Homeostasis
14.2The Kidney
14.3Cell Signalling
14.4Blood Glucose Concentration
14.5Homeostasis in Plants
15Control & Coordination (A2 Only)
15.1Control & Coordination in Mammals
15.1.1Neurones
15.1.2Receptors
15.1.3Taste
15.1.4Reflexes
15.1.5Action Potentials
15.1.6Saltatory Conduction
15.1.7Synapses
15.1.8Cholinergic Synnapses
15.1.9Neuromuscular Junction
15.1.10Skeletal Muscle
15.1.11Sliding Filament Theory Contraction
15.1.12Sliding Filament Theory Contraction 2
15.1.13Menstruation
15.1.14Contraceptive Pill
15.2Control & Co-Ordination in Plants
16Inherited Change (A2 Only)
16.1Passage of Information to Offspring
16.2Genes & Phenotype
17Selection & Evolution (A2 Only)
17.2Natural & Artificial Selection
18Classification & Conservation (A2 Only)
18.1Biodiversity
18.2Classification
19Genetic Technology (A2 Only)
19.1Manipulating Genomes
19.2Genetic Technology Applied to Medicine
19.3Genetically Modified Organisms in Agriculture
Jump to other topics
1Cell Structure
1.1Cell Structure
1.1.1Studying Cells - Microscopes
1.1.2Introduction to Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.3Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells
1.1.4Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 2
1.1.5Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 3
1.1.6Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.7Viruses
1.1.8End of Topic Test - Cell Structure
1.1.9Exam-Style Question - Microscopes
1.1.10A-A* (AO2/3) - Cell Structure
2Biological Molecules
2.1Testing for Biological Modules
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
3Enzymes
4Cell Membranes & Transport
4.1Biological Membranes
5The Mitotic Cell Cycle
6Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis
6.1Nucleic Acids
7Transport in Plants
8Transport in Mammals
8.1Circulatory System
8.2Transport of Oxygen & Carbon Dioxide
9Gas Exchange
9.1Gas Exchange System
10Infectious Diseases
10.1Infectious Diseases
10.2Antibiotics
11Immunity
12Energy & Respiration (A2 Only)
13Photosynthesis (A2 Only)
14Homeostasis (A2 Only)
14.1Homeostasis
14.2The Kidney
14.3Cell Signalling
14.4Blood Glucose Concentration
14.5Homeostasis in Plants
15Control & Coordination (A2 Only)
15.1Control & Coordination in Mammals
15.1.1Neurones
15.1.2Receptors
15.1.3Taste
15.1.4Reflexes
15.1.5Action Potentials
15.1.6Saltatory Conduction
15.1.7Synapses
15.1.8Cholinergic Synnapses
15.1.9Neuromuscular Junction
15.1.10Skeletal Muscle
15.1.11Sliding Filament Theory Contraction
15.1.12Sliding Filament Theory Contraction 2
15.1.13Menstruation
15.1.14Contraceptive Pill
15.2Control & Co-Ordination in Plants
16Inherited Change (A2 Only)
16.1Passage of Information to Offspring
16.2Genes & Phenotype
17Selection & Evolution (A2 Only)
17.2Natural & Artificial Selection
18Classification & Conservation (A2 Only)
18.1Biodiversity
18.2Classification
19Genetic Technology (A2 Only)
19.1Manipulating Genomes
19.2Genetic Technology Applied to Medicine
19.3Genetically Modified Organisms in Agriculture
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books