2.4.1
Water Structure & Function
Function of Water
Function of Water
Water is a major component of cells and makes up 60-70% of the human body. Life evolved in an environment where water was abundant. It has several properties that are important in biology.


Importance of water
Importance of water
- Water is one of the most useful molecules for life. Its uses include:
- As a reactant in cells (e.g. photosynthesis, hydrolysis).
- Provides structural support in cells.
- Keeps organisms cool to maintain an optimum body temperature.


Properties of water
Properties of water
- Special properties of water are:
- Metabolic importance.
- High heat capacity.
- Heat of vaporization.
- Cohesive properties.
- Useful as a solvent.
The Structure of Water
The Structure of Water
The structure of a water molecule helps us to understand hydrogen bonding and the function of water.


Contents of a water molecule
Contents of a water molecule
- Water molecules (H2O) are made from:
- One oxygen atom.
- Two hydrogen atoms.


Polarity
Polarity
- Water is a polar molecule.
- The oxygen atoms in water are slightly negatively charged.
- The hydrogen atoms in water are slightly positively charged.


Hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonding
- The polarity of water molecules means that a hydrogen atom on one water molecule is attracted to the oxygen atom on another water molecule.
- This attraction is called hydrogen bonding.
Useful Properties of Water
Useful Properties of Water
Water is a major component of cells and is essential to life as we know it (60–70% of the human body is made up of water). The properties of water that make it such a useful substance are:


High latent heat of vaporisation
High latent heat of vaporisation
- The latent heat of vaporisation is the amount of energy needed to change one gram of a liquid substance to a gas.
- As liquid water heats up, hydrogen bonding makes it difficult to separate the water molecules from each other. This means that a lot of energy is needed for water to evaporate.
- When water evaporates, energy is used up - this cools the environment where the evaporation is taking place.
- This is why sweating helps with body temperature regulation.


High heat capacity
High heat capacity
- Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat one kilogram of a substance must absorb or lose to change its temperature by 1oC.
- Water has a high heat capacity so takes a long time to heat and cool.
- The specific heat capacity of water is much larger than sand. This is why land cools faster than the sea.
- Water is used by warm blooded animals to more evenly disperse heat in their bodies.
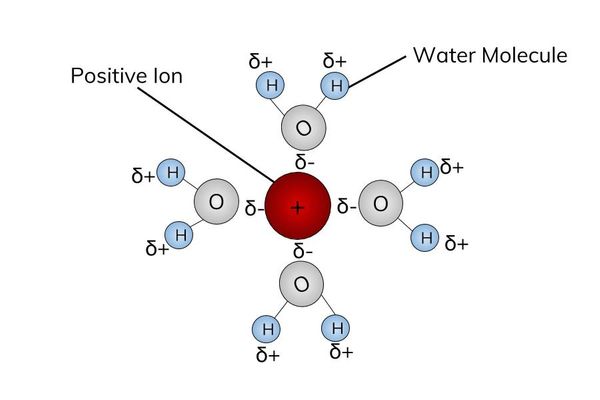

Good solvent
Good solvent
- Water is a good solvent because ions and polar molecules can easily dissolve in it.
- Water is a polar molecule. This means that the positive end of the water molecule attracts negative ions and the negative end will attract positive ions.


Good metabolite
Good metabolite
- Water is used or formed in many metabolic reactions, such as condensation and hydrolysis reactions.
- ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi + energy
- A bond is broken and a water molecule is used up and so this is a hydrolysis reaction.
- ADP + Pi + energy → ATP + H2O
- A new bond is formed and a water molecule is released and so this is a condensation reaction.
- ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi + energy
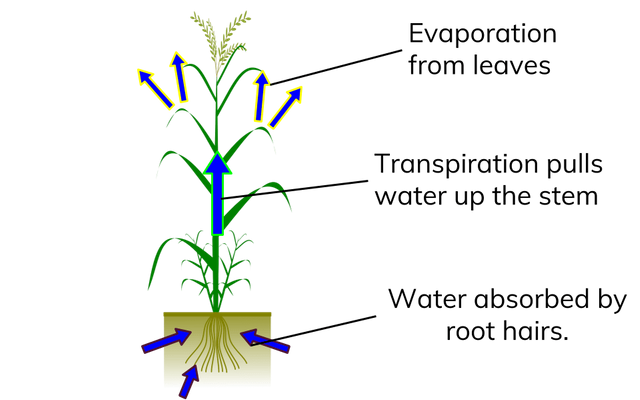

Cohesive properties
Cohesive properties
- The strong attraction between water molecules due to hydrogen bonds is called cohesion.
- Cohesion produces surface tension where water meets air.
- This is why water forms droplets when placed on a dry surface rather than being flattened out by gravity.
- Plants use this natural phenomenon to help transport water from their roots to their leaves.
1Cell Structure
1.1Cell Structure
1.1.1Studying Cells - Microscopes
1.1.2Introduction to Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.3Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells
1.1.4Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 2
1.1.5Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 3
1.1.6Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.7Viruses
1.1.8End of Topic Test - Cell Structure
1.1.9Exam-Style Question - Microscopes
1.1.10A-A* (AO2/3) - Cell Structure
2Biological Molecules
2.1Testing for Biological Modules
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
3Enzymes
4Cell Membranes & Transport
4.1Biological Membranes
5The Mitotic Cell Cycle
6Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis
6.1Nucleic Acids
7Transport in Plants
8Transport in Mammals
8.1Circulatory System
8.2Transport of Oxygen & Carbon Dioxide
9Gas Exchange
9.1Gas Exchange System
10Infectious Diseases
10.1Infectious Diseases
10.2Antibiotics
11Immunity
12Energy & Respiration (A2 Only)
13Photosynthesis (A2 Only)
14Homeostasis (A2 Only)
14.1Homeostasis
14.2The Kidney
14.3Cell Signalling
14.4Blood Glucose Concentration
14.5Homeostasis in Plants
15Control & Coordination (A2 Only)
15.1Control & Coordination in Mammals
15.1.1Neurones
15.1.2Receptors
15.1.3Taste
15.1.4Reflexes
15.1.5Action Potentials
15.1.6Saltatory Conduction
15.1.7Synapses
15.1.8Cholinergic Synnapses
15.1.9Neuromuscular Junction
15.1.10Skeletal Muscle
15.1.11Sliding Filament Theory Contraction
15.1.12Sliding Filament Theory Contraction 2
15.1.13Menstruation
15.1.14Contraceptive Pill
15.2Control & Co-Ordination in Plants
16Inherited Change (A2 Only)
16.1Passage of Information to Offspring
16.2Genes & Phenotype
17Selection & Evolution (A2 Only)
17.2Natural & Artificial Selection
18Classification & Conservation (A2 Only)
18.1Biodiversity
18.2Classification
19Genetic Technology (A2 Only)
19.1Manipulating Genomes
19.2Genetic Technology Applied to Medicine
19.3Genetically Modified Organisms in Agriculture
Jump to other topics
1Cell Structure
1.1Cell Structure
1.1.1Studying Cells - Microscopes
1.1.2Introduction to Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.3Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells
1.1.4Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 2
1.1.5Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 3
1.1.6Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.7Viruses
1.1.8End of Topic Test - Cell Structure
1.1.9Exam-Style Question - Microscopes
1.1.10A-A* (AO2/3) - Cell Structure
2Biological Molecules
2.1Testing for Biological Modules
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
3Enzymes
4Cell Membranes & Transport
4.1Biological Membranes
5The Mitotic Cell Cycle
6Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis
6.1Nucleic Acids
7Transport in Plants
8Transport in Mammals
8.1Circulatory System
8.2Transport of Oxygen & Carbon Dioxide
9Gas Exchange
9.1Gas Exchange System
10Infectious Diseases
10.1Infectious Diseases
10.2Antibiotics
11Immunity
12Energy & Respiration (A2 Only)
13Photosynthesis (A2 Only)
14Homeostasis (A2 Only)
14.1Homeostasis
14.2The Kidney
14.3Cell Signalling
14.4Blood Glucose Concentration
14.5Homeostasis in Plants
15Control & Coordination (A2 Only)
15.1Control & Coordination in Mammals
15.1.1Neurones
15.1.2Receptors
15.1.3Taste
15.1.4Reflexes
15.1.5Action Potentials
15.1.6Saltatory Conduction
15.1.7Synapses
15.1.8Cholinergic Synnapses
15.1.9Neuromuscular Junction
15.1.10Skeletal Muscle
15.1.11Sliding Filament Theory Contraction
15.1.12Sliding Filament Theory Contraction 2
15.1.13Menstruation
15.1.14Contraceptive Pill
15.2Control & Co-Ordination in Plants
16Inherited Change (A2 Only)
16.1Passage of Information to Offspring
16.2Genes & Phenotype
17Selection & Evolution (A2 Only)
17.2Natural & Artificial Selection
18Classification & Conservation (A2 Only)
18.1Biodiversity
18.2Classification
19Genetic Technology (A2 Only)
19.1Manipulating Genomes
19.2Genetic Technology Applied to Medicine
19.3Genetically Modified Organisms in Agriculture
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books