2.2.2
Carbohydrates
Types of Monosaccharides
Types of Monosaccharides
Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. They are made from monosaccharides, which are simple sugars containing three to seven carbon atoms.
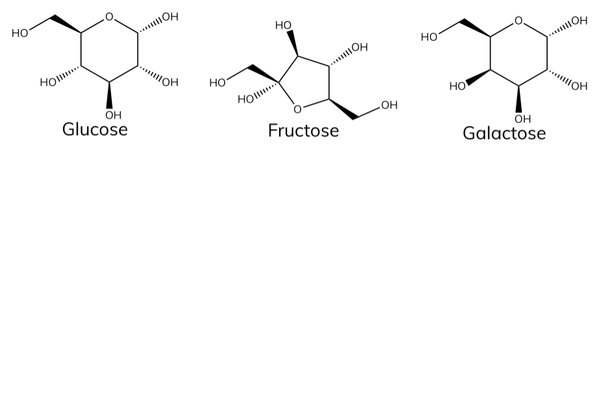

Examples of monosaccharides
Examples of monosaccharides
- Monosaccharides are simple sugars. Examples include:
- Glucose.
- Galactose (found in milk).
- Fructose (found in fruit).
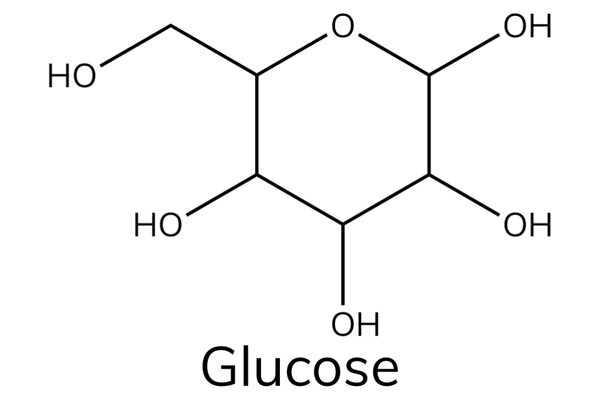

Glucose
Glucose
- Glucose is a hexose sugar that has the chemical formula C6H12O6.
- Glucose is an important source of energy in humans.
- During cellular respiration, the energy released from glucose helps to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
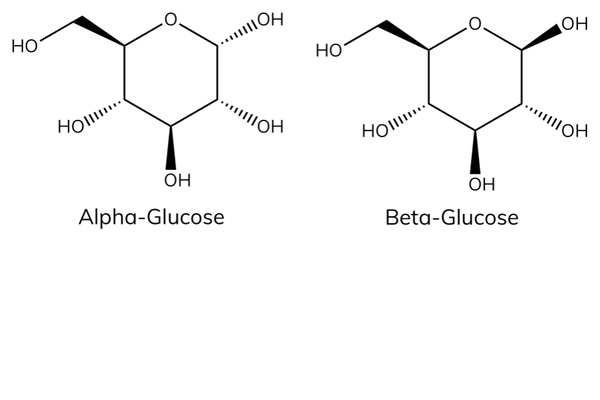

Alpha vs beta glucose
Alpha vs beta glucose
- Alpha- and beta-glucose are isomers. Isomers have the same molecular formula but a different arrangement of atoms in space.
- The carbon atoms are numbered from 1 – 6 and the OH (hydroxyl) groups are in a different orientation around C1.
-min,h_400,q_80,w_640.jpg)
-min,h_400,q_80,w_640.jpg)
Hexose vs pentose sugars
Hexose vs pentose sugars
- Glucose is an example of a hexose sugar, as it has six carbons in its structure.
- Pentose sugars are monosaccharides that have five carbon atoms in their structure, for example, ribose.
- Ribose is one of the three main components of the nucleotides found in RNA.
Disaccharides and Polysaccharides
Disaccharides and Polysaccharides
When two monosaccharides join via a condensation reaction, they form a disaccharide. When more than two monosaccharides join together, they form a polysaccharide chain.
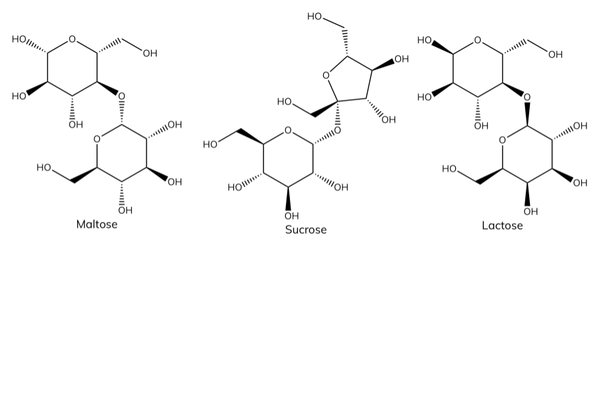

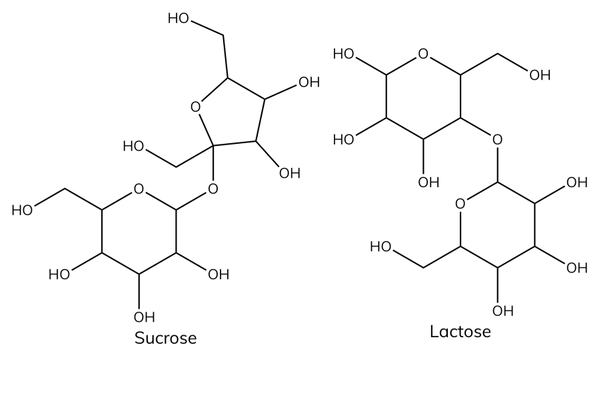
Examples of disaccharides
Examples of disaccharides
- Glucose + glucose → maltose.
- Glucose + fructose → sucrose.
- Glucose + galactose → lactose.

Functions of disaccharides
Functions of disaccharides
- Sucrose is common table sugar.
- Lactose is the sugar found in milk.
- Lactose intolerance is a common problem where the body is unable to digest lactose.
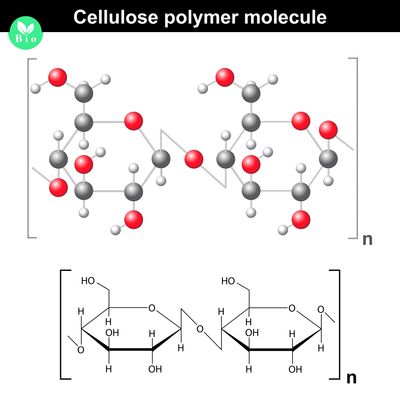

Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides
- Polysaccharides are made up of two or more monosaccharides joined together by glycosidic bonds.
- The chain may be branched or unbranched.
- The chain may contain different types of monosaccharides.
- Starch, glycogen, cellulose and chitin are examples of polysaccharides.


Glycosidic bonds
Glycosidic bonds
- Monosaccharides such as glucose can form covalent glycosidic bonds with neighbouring monosaccharide molecules to form carbohydrate polymers known as polysaccharides.
- -OH groups from neighbouring monosaccharides undergo a condensation reaction to form an O-link between the two monosaccharides, with water being released.
- To break a glycosidic bond, the reverse reaction occurs during which water is added.
- This is called a hydrolysis reaction.


Reducing vs non-reducing sugars
Reducing vs non-reducing sugars
- Maltose, glucose, and fructose are reducing sugars.
- Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar.
1Cell Structure
1.1Cell Structure
1.1.1Studying Cells - Microscopes
1.1.2Introduction to Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.3Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells
1.1.4Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 2
1.1.5Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 3
1.1.6Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.7Viruses
1.1.8End of Topic Test - Cell Structure
1.1.9Exam-Style Question - Microscopes
1.1.10A-A* (AO2/3) - Cell Structure
2Biological Molecules
2.1Testing for Biological Modules
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
3Enzymes
4Cell Membranes & Transport
4.1Biological Membranes
5The Mitotic Cell Cycle
6Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis
6.1Nucleic Acids
7Transport in Plants
8Transport in Mammals
8.1Circulatory System
8.2Transport of Oxygen & Carbon Dioxide
9Gas Exchange
9.1Gas Exchange System
10Infectious Diseases
10.1Infectious Diseases
10.2Antibiotics
11Immunity
12Energy & Respiration (A2 Only)
13Photosynthesis (A2 Only)
14Homeostasis (A2 Only)
14.1Homeostasis
14.2The Kidney
14.3Cell Signalling
14.4Blood Glucose Concentration
14.5Homeostasis in Plants
15Control & Coordination (A2 Only)
15.1Control & Coordination in Mammals
15.1.1Neurones
15.1.2Receptors
15.1.3Taste
15.1.4Reflexes
15.1.5Action Potentials
15.1.6Saltatory Conduction
15.1.7Synapses
15.1.8Cholinergic Synnapses
15.1.9Neuromuscular Junction
15.1.10Skeletal Muscle
15.1.11Sliding Filament Theory Contraction
15.1.12Sliding Filament Theory Contraction 2
15.1.13Menstruation
15.1.14Contraceptive Pill
15.2Control & Co-Ordination in Plants
16Inherited Change (A2 Only)
16.1Passage of Information to Offspring
16.2Genes & Phenotype
17Selection & Evolution (A2 Only)
17.2Natural & Artificial Selection
18Classification & Conservation (A2 Only)
18.1Biodiversity
18.2Classification
19Genetic Technology (A2 Only)
19.1Manipulating Genomes
19.2Genetic Technology Applied to Medicine
19.3Genetically Modified Organisms in Agriculture
Jump to other topics
1Cell Structure
1.1Cell Structure
1.1.1Studying Cells - Microscopes
1.1.2Introduction to Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.3Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells
1.1.4Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 2
1.1.5Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 3
1.1.6Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.7Viruses
1.1.8End of Topic Test - Cell Structure
1.1.9Exam-Style Question - Microscopes
1.1.10A-A* (AO2/3) - Cell Structure
2Biological Molecules
2.1Testing for Biological Modules
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
3Enzymes
4Cell Membranes & Transport
4.1Biological Membranes
5The Mitotic Cell Cycle
6Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis
6.1Nucleic Acids
7Transport in Plants
8Transport in Mammals
8.1Circulatory System
8.2Transport of Oxygen & Carbon Dioxide
9Gas Exchange
9.1Gas Exchange System
10Infectious Diseases
10.1Infectious Diseases
10.2Antibiotics
11Immunity
12Energy & Respiration (A2 Only)
13Photosynthesis (A2 Only)
14Homeostasis (A2 Only)
14.1Homeostasis
14.2The Kidney
14.3Cell Signalling
14.4Blood Glucose Concentration
14.5Homeostasis in Plants
15Control & Coordination (A2 Only)
15.1Control & Coordination in Mammals
15.1.1Neurones
15.1.2Receptors
15.1.3Taste
15.1.4Reflexes
15.1.5Action Potentials
15.1.6Saltatory Conduction
15.1.7Synapses
15.1.8Cholinergic Synnapses
15.1.9Neuromuscular Junction
15.1.10Skeletal Muscle
15.1.11Sliding Filament Theory Contraction
15.1.12Sliding Filament Theory Contraction 2
15.1.13Menstruation
15.1.14Contraceptive Pill
15.2Control & Co-Ordination in Plants
16Inherited Change (A2 Only)
16.1Passage of Information to Offspring
16.2Genes & Phenotype
17Selection & Evolution (A2 Only)
17.2Natural & Artificial Selection
18Classification & Conservation (A2 Only)
18.1Biodiversity
18.2Classification
19Genetic Technology (A2 Only)
19.1Manipulating Genomes
19.2Genetic Technology Applied to Medicine
19.3Genetically Modified Organisms in Agriculture
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books