2.1.1
Tests for Sugars & Starch
Benedict's Test for Sugars
Benedict's Test for Sugars
Benedict’s solution (also known as Benedict's reagent or the Benedict’s test) can be used as a test for reducing and non-reducing sugars.


Reducing sugars
Reducing sugars
- All monosaccharides are reducing sugars.
- E.g. Glucose, galactose and fructose.
- Some disaccharides are reducing sugars.
- E.g. Lactose and maltose.
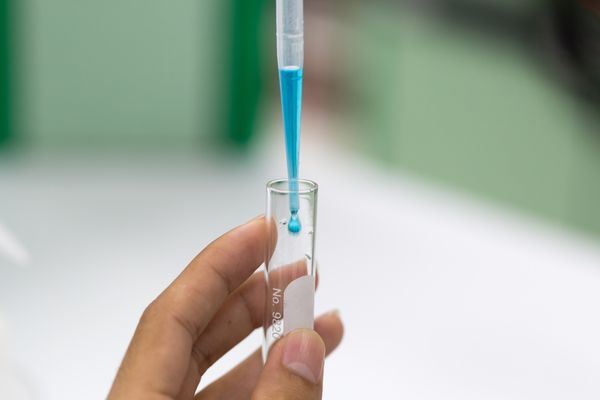

Test for reducing sugars
Test for reducing sugars
- Benedict's solution can be reduced by reducing sugars.
- Benedict's solution is a clear blue liquid that changes colour and gives a precipitate depending on how much it is reduced.
- Step 1: Place 2 ml of the substance in a boiling tube (substance must be in liquid form).
- Step 2: Add 10 drops of Benedict's solution.
- Step 3: Place in a boiling water bath for 3-5 minutes.


Results of the Benedict's test
Results of the Benedict's test
- Blue solution → no reducing sugar.
- Green/yellow precipitate → traces of reducing sugar.
- Orange/red precipitate → moderate amounts of reducing sugar.
- Brick red precipitate → large amount of reducing sugar.
- The faster the colour change occurs, the greater the concentration of reducing sugar present.
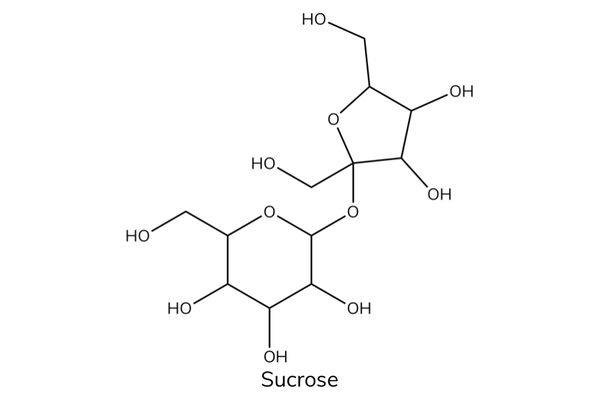

Non-reducing sugars
Non-reducing sugars
- Non-reducing sugars will show a negative result to the Benedict’s test. A second test is needed to determine if non-reducing sugar is present.
- Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar. It is a disaccharide made up of glucose and fructose joined by a glycosidic bond.


Test for non-reducing sugars
Test for non-reducing sugars
- Step 1: Boil in dilute HCl (to hydrolyse the non-reducing sugar).
- Step 2: Neutralise the solution by adding sodium bicarbonate.
- Step 3: Repeat the Benedict’s test.
- The result will now be positive if a non-reducing sugar is present.
- If the solution remains blue, then no sugar is present.
The Iodine Test for Starch
The Iodine Test for Starch
A common test for the presence of starch, particularly in food testing, is to add iodine. Iodine is commonly used as a name for a solution of potassium iodide.


Step 1
Step 1
- Place a small sample into the dimple of a spotting tile or into a boiling tube.


Step 2
Step 2
- Add a few drops of iodine and observe any colour change.


Results
Results
- If starch is present, the solution will change colour from orange → blue-black.
1Cell Structure
1.1Cell Structure
1.1.1Studying Cells - Microscopes
1.1.2Introduction to Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.3Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells
1.1.4Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 2
1.1.5Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 3
1.1.6Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.7Viruses
1.1.8End of Topic Test - Cell Structure
1.1.9Exam-Style Question - Microscopes
1.1.10A-A* (AO2/3) - Cell Structure
2Biological Molecules
2.1Testing for Biological Modules
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
3Enzymes
4Cell Membranes & Transport
4.1Biological Membranes
5The Mitotic Cell Cycle
6Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis
6.1Nucleic Acids
7Transport in Plants
8Transport in Mammals
8.1Circulatory System
8.2Transport of Oxygen & Carbon Dioxide
9Gas Exchange
9.1Gas Exchange System
10Infectious Diseases
10.1Infectious Diseases
10.2Antibiotics
11Immunity
12Energy & Respiration (A2 Only)
13Photosynthesis (A2 Only)
14Homeostasis (A2 Only)
14.1Homeostasis
14.2The Kidney
14.3Cell Signalling
14.4Blood Glucose Concentration
14.5Homeostasis in Plants
15Control & Coordination (A2 Only)
15.1Control & Coordination in Mammals
15.1.1Neurones
15.1.2Receptors
15.1.3Taste
15.1.4Reflexes
15.1.5Action Potentials
15.1.6Saltatory Conduction
15.1.7Synapses
15.1.8Cholinergic Synnapses
15.1.9Neuromuscular Junction
15.1.10Skeletal Muscle
15.1.11Sliding Filament Theory Contraction
15.1.12Sliding Filament Theory Contraction 2
15.1.13Menstruation
15.1.14Contraceptive Pill
15.2Control & Co-Ordination in Plants
16Inherited Change (A2 Only)
16.1Passage of Information to Offspring
16.2Genes & Phenotype
17Selection & Evolution (A2 Only)
17.2Natural & Artificial Selection
18Classification & Conservation (A2 Only)
18.1Biodiversity
18.2Classification
19Genetic Technology (A2 Only)
19.1Manipulating Genomes
19.2Genetic Technology Applied to Medicine
19.3Genetically Modified Organisms in Agriculture
Jump to other topics
1Cell Structure
1.1Cell Structure
1.1.1Studying Cells - Microscopes
1.1.2Introduction to Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.3Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells
1.1.4Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 2
1.1.5Ultrastructure of Eukaryotic Cells 3
1.1.6Prokaryotic Cells
1.1.7Viruses
1.1.8End of Topic Test - Cell Structure
1.1.9Exam-Style Question - Microscopes
1.1.10A-A* (AO2/3) - Cell Structure
2Biological Molecules
2.1Testing for Biological Modules
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
3Enzymes
4Cell Membranes & Transport
4.1Biological Membranes
5The Mitotic Cell Cycle
6Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis
6.1Nucleic Acids
7Transport in Plants
8Transport in Mammals
8.1Circulatory System
8.2Transport of Oxygen & Carbon Dioxide
9Gas Exchange
9.1Gas Exchange System
10Infectious Diseases
10.1Infectious Diseases
10.2Antibiotics
11Immunity
12Energy & Respiration (A2 Only)
13Photosynthesis (A2 Only)
14Homeostasis (A2 Only)
14.1Homeostasis
14.2The Kidney
14.3Cell Signalling
14.4Blood Glucose Concentration
14.5Homeostasis in Plants
15Control & Coordination (A2 Only)
15.1Control & Coordination in Mammals
15.1.1Neurones
15.1.2Receptors
15.1.3Taste
15.1.4Reflexes
15.1.5Action Potentials
15.1.6Saltatory Conduction
15.1.7Synapses
15.1.8Cholinergic Synnapses
15.1.9Neuromuscular Junction
15.1.10Skeletal Muscle
15.1.11Sliding Filament Theory Contraction
15.1.12Sliding Filament Theory Contraction 2
15.1.13Menstruation
15.1.14Contraceptive Pill
15.2Control & Co-Ordination in Plants
16Inherited Change (A2 Only)
16.1Passage of Information to Offspring
16.2Genes & Phenotype
17Selection & Evolution (A2 Only)
17.2Natural & Artificial Selection
18Classification & Conservation (A2 Only)
18.1Biodiversity
18.2Classification
19Genetic Technology (A2 Only)
19.1Manipulating Genomes
19.2Genetic Technology Applied to Medicine
19.3Genetically Modified Organisms in Agriculture
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books