6.5.6
Types of Synapse
Neuromuscular Junction
Neuromuscular Junction
A neuromuscular junction is a synapse between a motor neurone and a muscle cell. An action potential is transmitted across the synapse using the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. The steps involved are:


Arrival at the synaptic knob
Arrival at the synaptic knob
- An action potential arrives at the synaptic knob at the end of the motor neurone.
- The action potential depolarises the membrane of the synaptic knob. This causes voltage-gated calcium (Ca2+) ion channels to open.
- Ca2+ ions diffuse into the synaptic knob.


Release of acetylcholine (ACh)
Release of acetylcholine (ACh)
- The Ca2+ ion concentration inside the synaptic knob begins to increase.
- This causes the synaptic vesicles to move and fuse with the presynaptic membrane.
- Acetylcholine, the neurotransmitter inside the vesicles, is released into the synaptic cleft.
- This process is called exocytosis.


Binding to receptors
Binding to receptors
- Acetylcholine binds to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane called nicotinic cholinergic receptors.
- Binding of the neurotransmitter opens sodium ion channels in the postsynaptic muscle cell.
- As Na+ ions diffuse into the cell, the membrane becomes depolarised.
- If the potential difference reaches the threshold value, an action potential is generated and flows along the motor cell.


Removal of acetylcholine
Removal of acetylcholine
- An enzyme called acetylcholinesterase (AChE) breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft.
- The products of the break down are reabsorbed by the presynaptic neurone and reused to synthesise more acetylcholine.
- It is important that the acetylcholine is removed from the receptors. This stops action potentials from being continuously generated in the postsynaptic cell.
Cholinergic Synapses
Cholinergic Synapses
Synapses that use acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter are called cholinergic synapses. Although acetylcholine is also used at a neuromuscular junction, there are some key differences:


Type of postsynaptic cell
Type of postsynaptic cell
- Cholinergic synapses are between two neurones.
- Neuromuscular junctions are between a motor neurone and a muscle cell.


Number of receptors
Number of receptors
- There are less receptors in the postsynaptic membrane at a cholinergic synapse than at a neuromuscular junction.


Type of response
Type of response
- A cholinergic synapse can trigger an inhibitory or excitatory response in the postsynaptic membrane.
- An action potential at a neuromuscular junction always triggers an excitatory response in the muscle cell.
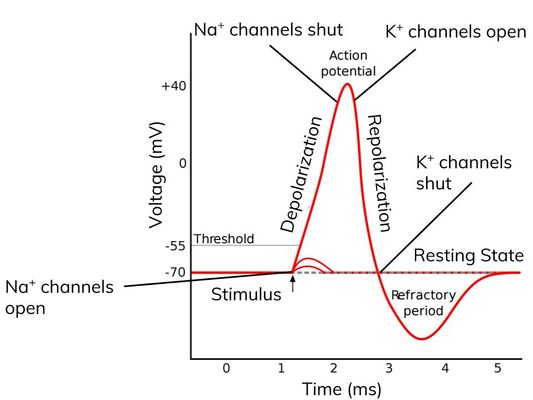

Result of depolarisation
Result of depolarisation
- In a cholinergic synapse, depolarisation of the postsynaptic membrane results in an action potential.
- At a neuromuscular junction, depolarisation of the postsynaptic membrane results in muscle contraction.
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase
- Acetylcholinesterase is the enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine after it has bound to the receptors on the postsynaptic membrane.
- In cholinergic synapses, the enzyme is located in the synaptic cleft.
- At a neuromuscular junction, the enzyme is stored in clefts in the postsynaptic membrane.
1Cell Biology
1.1Introduction to Cells
1.2Ultrastructure of Cells
1.3Membrane Structure
1.4Membrane Transport
1.5The Origin of Cells
2Molecular Biology
2.1Water
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
2.4Enzymes
2.5Structure of DNA & RNA
2.6DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation
2.7Cell Respiration
2.8Photosynthesis
3Genetics
3.1Genes
3.2Chromosomes
3.3Meiosis
3.4Inheritance
3.5Genetic Modification & Biotechnology
4Ecology
4.1Species, Communities & Ecosytems
4.3Carbon Cycle
5Evolution & Biodiversity
5.1Evidence for Evolution
5.2Natural Selection
5.3Classification of Biodiversity
6Human Physiology
6.1Digestion & Absorption
6.2The Blood System
6.3Defence Against Infectious Disease
6.5Neurons & Synapses
7AHL: Nucleic Acids
7.1DNA Structure & Replication
7.2Transcription & Gene Expression
8AHL: Metabolism, Cell Respiration & Photosynthesis
8.1Metabolism
8.2Cell Respiration
9AHL: Plant Biology
9.1Transport in the Xylem of Plants
9.2Transport in the Phloem of Plants
9.3Growth in Plants
10AHL: Genetics & Evolution
10.1Meiosis
10.2Inheritance
10.2.1Linked Genes
10.2.2Sex-Linked Genes
10.2.3Non-Nuclear Inheritance
10.2.4Chi-Squared Test
10.2.5End of Topic Quiz - Inheritance
10.2.6IB Multiple Choice - Non-Mendelian Genetics
10.2.7Introduction to Non-Mendelian Inheritance
10.2.8Extended Response - Inheritance
10.2.9Grade 4-5 (Scientific Practices) - Inheritance
11AHL: Animal Physiology
11.1Antibody Production & Vaccination
11.3The Kidney & Osmoregulation
Jump to other topics
1Cell Biology
1.1Introduction to Cells
1.2Ultrastructure of Cells
1.3Membrane Structure
1.4Membrane Transport
1.5The Origin of Cells
2Molecular Biology
2.1Water
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
2.4Enzymes
2.5Structure of DNA & RNA
2.6DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation
2.7Cell Respiration
2.8Photosynthesis
3Genetics
3.1Genes
3.2Chromosomes
3.3Meiosis
3.4Inheritance
3.5Genetic Modification & Biotechnology
4Ecology
4.1Species, Communities & Ecosytems
4.3Carbon Cycle
5Evolution & Biodiversity
5.1Evidence for Evolution
5.2Natural Selection
5.3Classification of Biodiversity
6Human Physiology
6.1Digestion & Absorption
6.2The Blood System
6.3Defence Against Infectious Disease
6.5Neurons & Synapses
7AHL: Nucleic Acids
7.1DNA Structure & Replication
7.2Transcription & Gene Expression
8AHL: Metabolism, Cell Respiration & Photosynthesis
8.1Metabolism
8.2Cell Respiration
9AHL: Plant Biology
9.1Transport in the Xylem of Plants
9.2Transport in the Phloem of Plants
9.3Growth in Plants
10AHL: Genetics & Evolution
10.1Meiosis
10.2Inheritance
10.2.1Linked Genes
10.2.2Sex-Linked Genes
10.2.3Non-Nuclear Inheritance
10.2.4Chi-Squared Test
10.2.5End of Topic Quiz - Inheritance
10.2.6IB Multiple Choice - Non-Mendelian Genetics
10.2.7Introduction to Non-Mendelian Inheritance
10.2.8Extended Response - Inheritance
10.2.9Grade 4-5 (Scientific Practices) - Inheritance
11AHL: Animal Physiology
11.1Antibody Production & Vaccination
11.3The Kidney & Osmoregulation
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books