5.2.1
Introduction
Principles of Natural Selection
Principles of Natural Selection
Natural selection is the process that leads to evolution in a population. In order to understand how this process functions, it is important to learn the key principles of natural selection.


Random mutation
Random mutation
- Mutations are changes in the gene sequence of DNA.
- Random mutations can arise spontaneously.
- New mutations can result in new alleles of a gene.


Variation in mutations
Variation in mutations
- Most mutations are harmful because they alter the normal functioning of a gene.
- But by chance, some mutations might confer a beneficial trait.
- An individual with a beneficial mutation will be more likely to survive and reproduce than an individual without the mutation.
-min,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
-min,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
Inheritance
Inheritance
- When an individual reproduces, their offspring will inherit half of their genes.
- When an individual with an advantageous mutation reproduces, the allele is inherited by their offspring.


Change in allele frequency
Change in allele frequency
- Individuals in the next generation who have the advantageous mutation are also more likely to reproduce and pass on the allele.
- Over many generations, the new allele will increase in frequency in the population.
- The change in allele frequency over time is called evolution.
Natural Selection and Evolution
Natural Selection and Evolution
Natural selection is the process where the frequency of alleles in a population changes over time. Natural selection is a process that gives rise to evolution.


Selective advantage
Selective advantage
- Genetic variation exists between individuals in a population.
- Some individuals will be more likely to survive (e.g. by being better at fighting disease) than others.
- Individuals that are better at surviving than others have a selective advantage.


Producing offspring
Producing offspring
- Individuals with a selective advantage are more likely to survive to reproduce than others.
- This means that the genes of an individual with a selective advantage are more likely to be passed onto offspring than the genes of an individual without a selective advantage.

Increasing allele frequencies
Increasing allele frequencies
- Individuals with a selective advantage are more likely to pass on their beneficial alleles than other individuals.
- The next generation is more likely to have alleles that provide a selective advantage than alleles that do not.
- This generation is also more likely to survive to reproduce and pass on their genes.
- This causes the alleles that provide a selective advantage to increase in frequency in the population.


Natural selection
Natural selection
- The process where the frequency of beneficial alleles increases over time is called natural selection.
- Natural selection controls the frequency of alleles in a population.
- If a harmful allele develops in an individual, this individual is less likely to survive and the harmful allele will decrease in frequency. This is also natural selection.
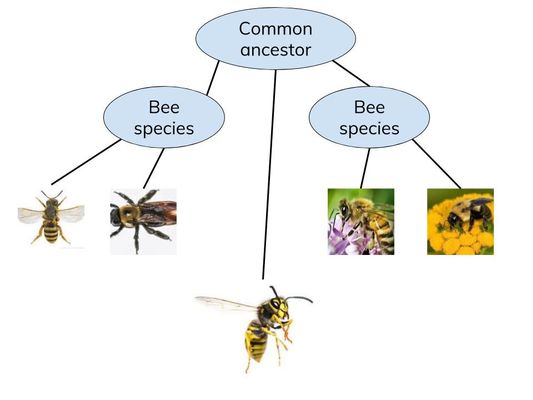

Evolution
Evolution
- The process of natural selection gives rise to evolution.
- Evolution is defined as a change in allele frequencies over time.
- E.g. The evolution of humans is the change in allele frequencies that has taken place over millions of years. This change has been driven by natural selection.
1Cell Biology
1.1Introduction to Cells
1.2Ultrastructure of Cells
1.3Membrane Structure
1.4Membrane Transport
1.5The Origin of Cells
2Molecular Biology
2.1Water
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
2.4Enzymes
2.5Structure of DNA & RNA
2.6DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation
2.7Cell Respiration
2.8Photosynthesis
3Genetics
3.1Genes
3.2Chromosomes
3.3Meiosis
3.4Inheritance
3.5Genetic Modification & Biotechnology
4Ecology
4.1Species, Communities & Ecosytems
4.3Carbon Cycle
5Evolution & Biodiversity
5.1Evidence for Evolution
5.2Natural Selection
5.3Classification of Biodiversity
6Human Physiology
6.1Digestion & Absorption
6.2The Blood System
6.3Defence Against Infectious Disease
6.5Neurons & Synapses
7AHL: Nucleic Acids
7.1DNA Structure & Replication
7.2Transcription & Gene Expression
8AHL: Metabolism, Cell Respiration & Photosynthesis
8.1Metabolism
8.2Cell Respiration
9AHL: Plant Biology
9.1Transport in the Xylem of Plants
9.2Transport in the Phloem of Plants
9.3Growth in Plants
10AHL: Genetics & Evolution
10.1Meiosis
10.2Inheritance
10.2.1Linked Genes
10.2.2Sex-Linked Genes
10.2.3Non-Nuclear Inheritance
10.2.4Chi-Squared Test
10.2.5End of Topic Quiz - Inheritance
10.2.6IB Multiple Choice - Non-Mendelian Genetics
10.2.7Introduction to Non-Mendelian Inheritance
10.2.8Extended Response - Inheritance
10.2.9Grade 4-5 (Scientific Practices) - Inheritance
11AHL: Animal Physiology
11.1Antibody Production & Vaccination
11.3The Kidney & Osmoregulation
Jump to other topics
1Cell Biology
1.1Introduction to Cells
1.2Ultrastructure of Cells
1.3Membrane Structure
1.4Membrane Transport
1.5The Origin of Cells
2Molecular Biology
2.1Water
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
2.4Enzymes
2.5Structure of DNA & RNA
2.6DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation
2.7Cell Respiration
2.8Photosynthesis
3Genetics
3.1Genes
3.2Chromosomes
3.3Meiosis
3.4Inheritance
3.5Genetic Modification & Biotechnology
4Ecology
4.1Species, Communities & Ecosytems
4.3Carbon Cycle
5Evolution & Biodiversity
5.1Evidence for Evolution
5.2Natural Selection
5.3Classification of Biodiversity
6Human Physiology
6.1Digestion & Absorption
6.2The Blood System
6.3Defence Against Infectious Disease
6.5Neurons & Synapses
7AHL: Nucleic Acids
7.1DNA Structure & Replication
7.2Transcription & Gene Expression
8AHL: Metabolism, Cell Respiration & Photosynthesis
8.1Metabolism
8.2Cell Respiration
9AHL: Plant Biology
9.1Transport in the Xylem of Plants
9.2Transport in the Phloem of Plants
9.3Growth in Plants
10AHL: Genetics & Evolution
10.1Meiosis
10.2Inheritance
10.2.1Linked Genes
10.2.2Sex-Linked Genes
10.2.3Non-Nuclear Inheritance
10.2.4Chi-Squared Test
10.2.5End of Topic Quiz - Inheritance
10.2.6IB Multiple Choice - Non-Mendelian Genetics
10.2.7Introduction to Non-Mendelian Inheritance
10.2.8Extended Response - Inheritance
10.2.9Grade 4-5 (Scientific Practices) - Inheritance
11AHL: Animal Physiology
11.1Antibody Production & Vaccination
11.3The Kidney & Osmoregulation
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books