2.4.1
Enzymes
Enzymes
Enzymes
Enzymes are proteins that catalyse reactions. The chemical reactants that enzymes bind to are called substrates.


Biological catalyst
Biological catalyst
- A substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being used up itself is a catalyst.
- Enzymes are proteins that catalyse biochemical reactions.
- Enzymes can act inside or outside of cells.
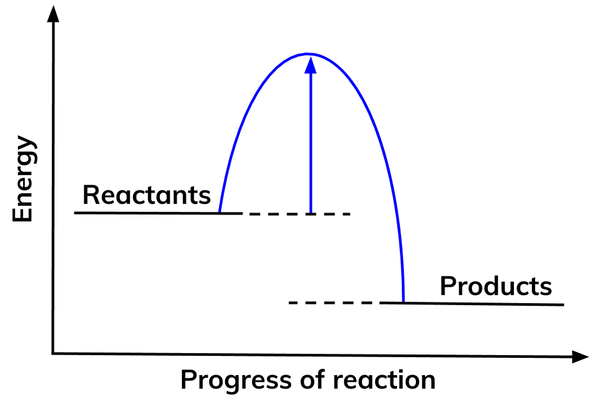

Activation energy
Activation energy
- For a chemical reaction to start, it needs a specific amount of energy. This amount of energy is different for different reactions.
- This is called the activation energy.
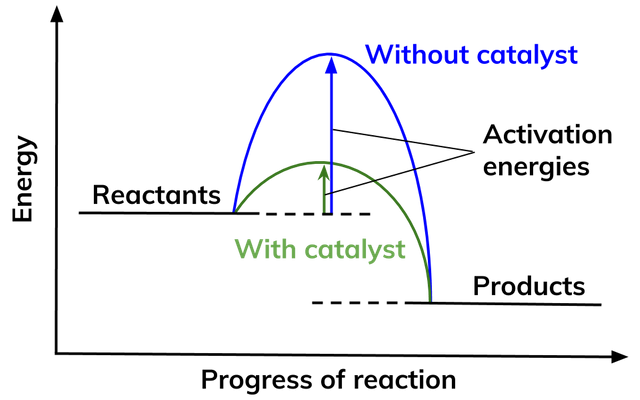

Activation energy and enzymes
Activation energy and enzymes
- Enzymes lower the activation energies of chemical reactions inside the cell to increase the rate of reactions.
- Enzymes lower the activation energy by binding to the reactant molecules (substrate) and allowing chemical bond-breaking and bond-forming processes to happen more easily.
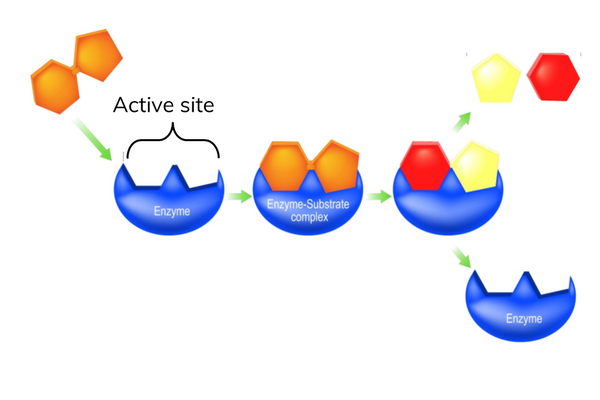

The active site
The active site
- Enzymes catalyse specific reactions.
- The active site has a specific shape for each enzyme.
- Substrates with a complementary shape to the active site of an enzyme can bind to form an enzyme-substrate complex.
- The shape of the active site is determined by the tertiary structure of the polypeptide.
Models of Enzyme Action
Models of Enzyme Action
Models of enzyme action have changed over time. For many years, it was thought that enzymes worked in a lock and key manner. The induced fit model is now more widely accepted.

The lock and key model
The lock and key model
- The lock and key model was originally used to explain enzyme action.
- The model proposes that the enzyme and substrate fit together perfectly.
- The substrate is a key fitting into a lock (the enzyme).
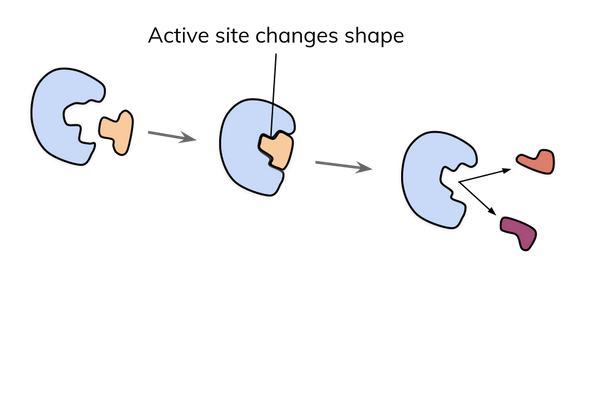

The induced fit model
The induced fit model
- The induced fit model suggests there is a more dynamic interaction between enzyme and substrate.
- The model states that as an enzyme and substrate come together, their interaction causes a small shift in the enzyme’s structure.
- The shift means that the enzyme and substrate can bind to form an enzyme-substrate complex and catalyse a reaction.
- This model is now more widely accepted.
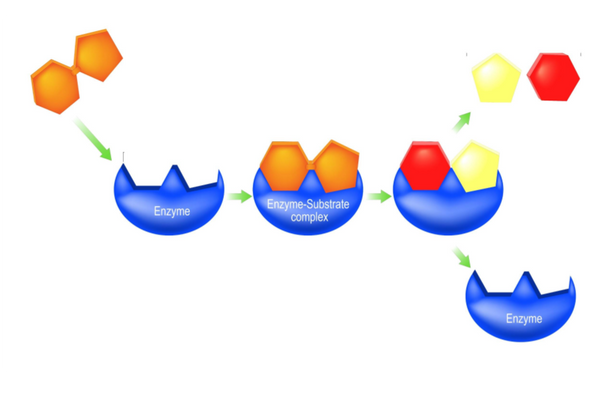
Enzyme-Substrate Complexes
Enzyme-Substrate Complexes
Enzymes bind with substrates to form an enzyme-substrate complex in a specific fashion. The specificity of enzymes is determined by two things:


Active site
Active site
- Every enzyme only catalyses one specific reaction.
- Every enzyme has a specific active site that is complementary to the specific substrate.
- This jigsaw puzzle-like match between an enzyme and its substrates is what makes enzymes highly specific.
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
,h_400,q_80,w_640.png)
Environmental factors
Environmental factors
- The 3D, tertiary structure of the polypetide chain determines the shape of the active site.
- Environmental changes can change the tertiary structure of the active site and can stop the enzyme from working properly.
- This is called a denatured enzyme.
1Cell Biology
1.1Introduction to Cells
1.2Ultrastructure of Cells
1.3Membrane Structure
1.4Membrane Transport
1.5The Origin of Cells
2Molecular Biology
2.1Water
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
2.4Enzymes
2.5Structure of DNA & RNA
2.6DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation
2.7Cell Respiration
2.8Photosynthesis
3Genetics
3.1Genes
3.2Chromosomes
3.3Meiosis
3.4Inheritance
3.5Genetic Modification & Biotechnology
4Ecology
4.1Species, Communities & Ecosytems
4.3Carbon Cycle
5Evolution & Biodiversity
5.1Evidence for Evolution
5.2Natural Selection
5.3Classification of Biodiversity
6Human Physiology
6.1Digestion & Absorption
6.2The Blood System
6.3Defence Against Infectious Disease
6.5Neurons & Synapses
7AHL: Nucleic Acids
7.1DNA Structure & Replication
7.2Transcription & Gene Expression
8AHL: Metabolism, Cell Respiration & Photosynthesis
8.1Metabolism
8.2Cell Respiration
9AHL: Plant Biology
9.1Transport in the Xylem of Plants
9.2Transport in the Phloem of Plants
9.3Growth in Plants
10AHL: Genetics & Evolution
10.1Meiosis
10.2Inheritance
10.2.1Linked Genes
10.2.2Sex-Linked Genes
10.2.3Non-Nuclear Inheritance
10.2.4Chi-Squared Test
10.2.5End of Topic Quiz - Inheritance
10.2.6IB Multiple Choice - Non-Mendelian Genetics
10.2.7Introduction to Non-Mendelian Inheritance
10.2.8Extended Response - Inheritance
10.2.9Grade 4-5 (Scientific Practices) - Inheritance
11AHL: Animal Physiology
11.1Antibody Production & Vaccination
11.3The Kidney & Osmoregulation
Jump to other topics
1Cell Biology
1.1Introduction to Cells
1.2Ultrastructure of Cells
1.3Membrane Structure
1.4Membrane Transport
1.5The Origin of Cells
2Molecular Biology
2.1Water
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
2.4Enzymes
2.5Structure of DNA & RNA
2.6DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation
2.7Cell Respiration
2.8Photosynthesis
3Genetics
3.1Genes
3.2Chromosomes
3.3Meiosis
3.4Inheritance
3.5Genetic Modification & Biotechnology
4Ecology
4.1Species, Communities & Ecosytems
4.3Carbon Cycle
5Evolution & Biodiversity
5.1Evidence for Evolution
5.2Natural Selection
5.3Classification of Biodiversity
6Human Physiology
6.1Digestion & Absorption
6.2The Blood System
6.3Defence Against Infectious Disease
6.5Neurons & Synapses
7AHL: Nucleic Acids
7.1DNA Structure & Replication
7.2Transcription & Gene Expression
8AHL: Metabolism, Cell Respiration & Photosynthesis
8.1Metabolism
8.2Cell Respiration
9AHL: Plant Biology
9.1Transport in the Xylem of Plants
9.2Transport in the Phloem of Plants
9.3Growth in Plants
10AHL: Genetics & Evolution
10.1Meiosis
10.2Inheritance
10.2.1Linked Genes
10.2.2Sex-Linked Genes
10.2.3Non-Nuclear Inheritance
10.2.4Chi-Squared Test
10.2.5End of Topic Quiz - Inheritance
10.2.6IB Multiple Choice - Non-Mendelian Genetics
10.2.7Introduction to Non-Mendelian Inheritance
10.2.8Extended Response - Inheritance
10.2.9Grade 4-5 (Scientific Practices) - Inheritance
11AHL: Animal Physiology
11.1Antibody Production & Vaccination
11.3The Kidney & Osmoregulation
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books