1.1.4
Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic Cells
All life on Earth exists as cells. A cell is the smallest unit of a living thing. All cells can be grouped into either eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells. These different categories have similarities and differences.


Similarities
Similarities
- Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells contain organelles.
- The cell-surface membrane in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is made of a phospholipid bilayer.
- This bilayer is responsible for controlling the passage of substances across exchange surfaces.


Differences
Differences
- Prokaryotic cells make up single-celled prokaryotic organisms (e.g. bacteria). In contrast, eukaryotic cells make up complex eukaryotic organisms (e.g. animals, plants, fungi and algae).
- Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells.
- Cells arise from other cells by binary fission in prokaryotic cells and by mitosis or meiosis in eukaryotic cells.
Types of Eukaryotic Cells
Types of Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells have similar structures across different types of organisms. But there are some key differences that are outlined here.


Animal cell
Animal cell
- Most animal cells have the following organelles:
- Mitochondria.
- Ribosomes.
- Endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
- Golgi.
- Lysosomes.
- Nucleus.
- Animal cells are enclosed by a cell membrane.
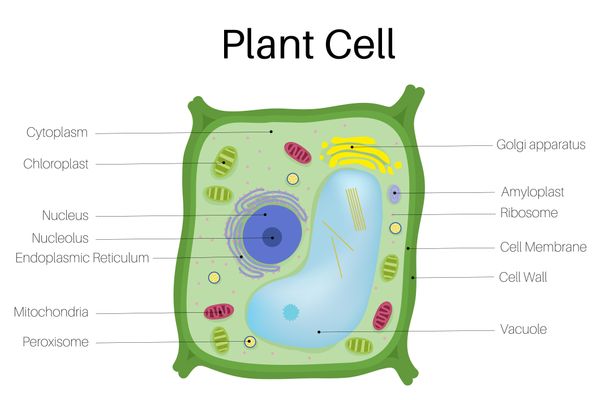

Plant cell
Plant cell
- Plant cells contain all the organelles found in animal cells.
- Plant cells also possess:
- Vacuole (a repository of cell sap).
- Chloroplasts (the site of photosynthesis).
- Cell wall (made of cellulose and contains plasmodesmata, through which cells exchange substances with each other).


Algal cells
Algal cells
- Algal cells and plant cells have an identical set of organelles.


Fungal cells
Fungal cells
- Fungal cells are similar to plant cells, apart from:
- There are no chloroplasts in fungal cells.
- The cell walls of fungal cells are made from chitin instead of cellulose.
Specialisation and Organisation of Cells
Specialisation and Organisation of Cells
In complex multicellular organisms, cells gain specific features. This is called specialisation. Specialised cells are then organised into groups to perform a function.


Cell specialisation
Cell specialisation
- A cell specialises because the shape and contents of a cell help it to carry out its function. Examples include:
- Muscle cells are very active so contain lots of mitochondria in order to produce ATP.
- Red blood cells have a biconcave shape and no nucleus to maximise space to carry oxygen. They also have lots of haemoglobin.
- Palisade cells have a long, upright shape and contain chlorophyll to absorb light for photosynthesis.


Cell organisation
Cell organisation
- Specialised cells are organised into tissues, tissues into organs and organs into organ systems.
- Tissues (e.g. muscle tissue, xylem tissue).
- Organs (e.g. the animal heart or plant leaf).
- Organ systems (e.g. the female reproductive system, which includes the uterus, ovaries, mammary glands and breasts).
1Cell Biology
1.1Introduction to Cells
1.2Ultrastructure of Cells
1.3Membrane Structure
1.4Membrane Transport
1.5The Origin of Cells
2Molecular Biology
2.1Water
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
2.4Enzymes
2.5Structure of DNA & RNA
2.6DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation
2.7Cell Respiration
2.8Photosynthesis
3Genetics
3.1Genes
3.2Chromosomes
3.3Meiosis
3.4Inheritance
3.5Genetic Modification & Biotechnology
4Ecology
4.1Species, Communities & Ecosytems
4.3Carbon Cycle
5Evolution & Biodiversity
5.1Evidence for Evolution
5.2Natural Selection
5.3Classification of Biodiversity
6Human Physiology
6.1Digestion & Absorption
6.2The Blood System
6.3Defence Against Infectious Disease
6.5Neurons & Synapses
7AHL: Nucleic Acids
7.1DNA Structure & Replication
7.2Transcription & Gene Expression
8AHL: Metabolism, Cell Respiration & Photosynthesis
8.1Metabolism
8.2Cell Respiration
9AHL: Plant Biology
9.1Transport in the Xylem of Plants
9.2Transport in the Phloem of Plants
9.3Growth in Plants
10AHL: Genetics & Evolution
10.1Meiosis
10.2Inheritance
10.2.1Linked Genes
10.2.2Sex-Linked Genes
10.2.3Non-Nuclear Inheritance
10.2.4Chi-Squared Test
10.2.5End of Topic Quiz - Inheritance
10.2.6IB Multiple Choice - Non-Mendelian Genetics
10.2.7Introduction to Non-Mendelian Inheritance
10.2.8Extended Response - Inheritance
10.2.9Grade 4-5 (Scientific Practices) - Inheritance
11AHL: Animal Physiology
11.1Antibody Production & Vaccination
11.3The Kidney & Osmoregulation
Jump to other topics
1Cell Biology
1.1Introduction to Cells
1.2Ultrastructure of Cells
1.3Membrane Structure
1.4Membrane Transport
1.5The Origin of Cells
2Molecular Biology
2.1Water
2.2Carbohydrates & Lipids
2.3Proteins
2.4Enzymes
2.5Structure of DNA & RNA
2.6DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation
2.7Cell Respiration
2.8Photosynthesis
3Genetics
3.1Genes
3.2Chromosomes
3.3Meiosis
3.4Inheritance
3.5Genetic Modification & Biotechnology
4Ecology
4.1Species, Communities & Ecosytems
4.3Carbon Cycle
5Evolution & Biodiversity
5.1Evidence for Evolution
5.2Natural Selection
5.3Classification of Biodiversity
6Human Physiology
6.1Digestion & Absorption
6.2The Blood System
6.3Defence Against Infectious Disease
6.5Neurons & Synapses
7AHL: Nucleic Acids
7.1DNA Structure & Replication
7.2Transcription & Gene Expression
8AHL: Metabolism, Cell Respiration & Photosynthesis
8.1Metabolism
8.2Cell Respiration
9AHL: Plant Biology
9.1Transport in the Xylem of Plants
9.2Transport in the Phloem of Plants
9.3Growth in Plants
10AHL: Genetics & Evolution
10.1Meiosis
10.2Inheritance
10.2.1Linked Genes
10.2.2Sex-Linked Genes
10.2.3Non-Nuclear Inheritance
10.2.4Chi-Squared Test
10.2.5End of Topic Quiz - Inheritance
10.2.6IB Multiple Choice - Non-Mendelian Genetics
10.2.7Introduction to Non-Mendelian Inheritance
10.2.8Extended Response - Inheritance
10.2.9Grade 4-5 (Scientific Practices) - Inheritance
11AHL: Animal Physiology
11.1Antibody Production & Vaccination
11.3The Kidney & Osmoregulation
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books
