6.1.1
Exponential Function
Exponential Functions
Exponential Functions
Functions that are linear show growth or decay that occurs at a steady rate. The exponential function models growth or decay with an increasing rate.
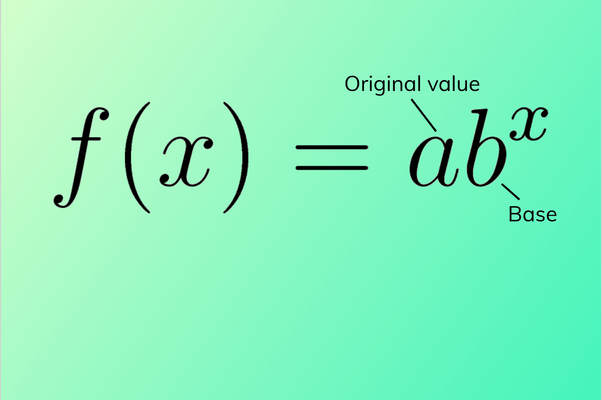
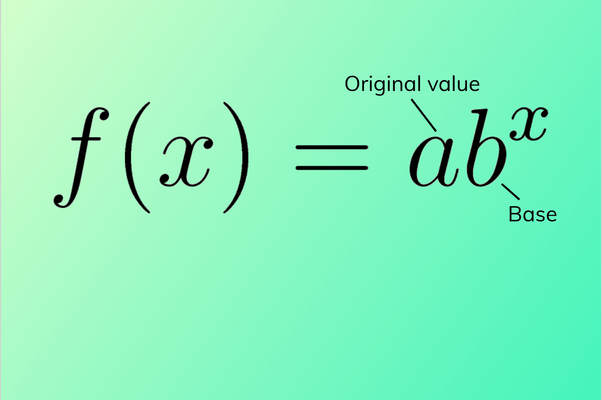
Definition
Definition
- For any real number , an exponential function is a function with the form"
- Where is a non-zero real number called the initial value and is any positive real number such that .
- We call the base of the exponential function.
- has base 3.

Exponential growth
Exponential growth
- Exponential growth means that the original value increases by the same percentage over equal increments found in the domain.
- As the value grows, so does the percentage of the value.
- Linear growth means the original value increases by the same amount over equal increments found in the domain.

Exponential growth
Exponential growth
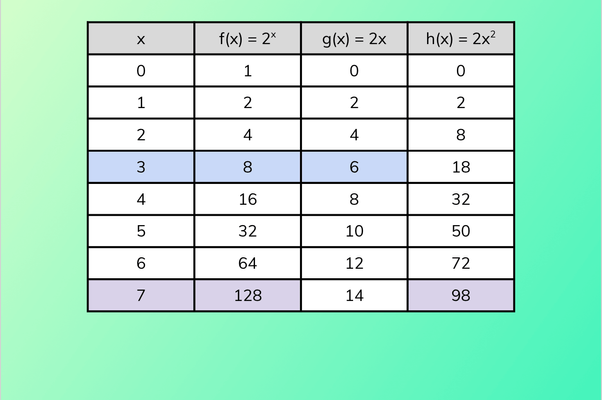
- The table shows the values for which the exponential function of base 2 is larger than linear and quadratic functions.
- In general, the exponential function will always eventually outgrow any polynomial.
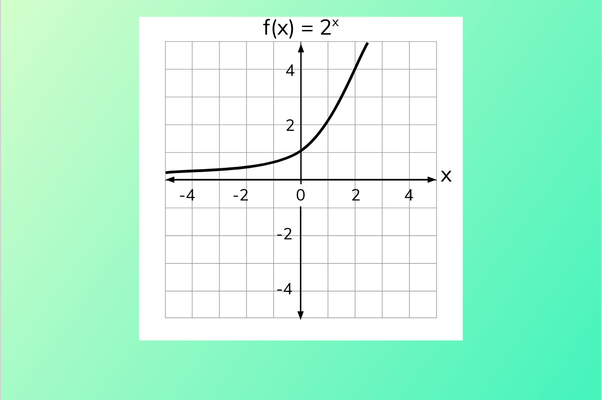

Graph
Graph
- The -intercept of an exponential function is
.
- For a function with no initial value such as , this intercept is always equal to 1.
- The graph does not cross the -axis, instead getting closer toward it for very large and negative values of .
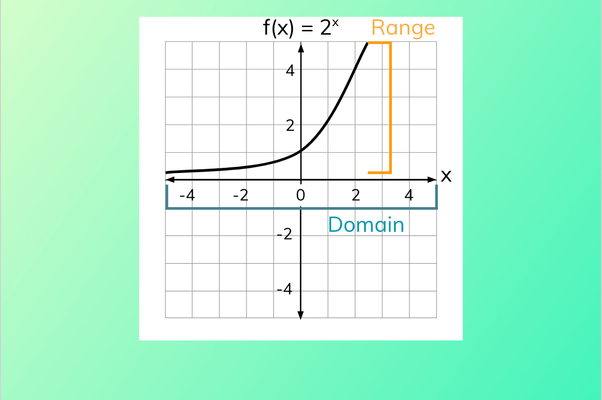

Properties
Properties
- The domain of is all of the real numbers.
- The range is all positive real numbers if .
- The range is all negative real numbers if .
1Proof
1.1Types of Numbers
1.2Notation
2Algebra & Functions
2.1Powers & Roots
2.2Quadratic Equations
2.3Inequalities
2.4Polynomials
2.5Graphs
2.7Transformation of Graphs
3Coordinate Geometry
3.1Straight Lines
3.2Circles
3.2.1Equations of Circles centred at Origin
3.2.2Finding the Centre & Radius
3.2.3Equation of a Tangent
3.2.4Circle Theorems - Perpendicular Bisector
3.2.5Circle Theorems - Angle at the Centre
3.2.6Circle Theorems - Angle at a Semi-Circle
3.2.7Equation of a Perpendicular Bisector
3.2.8Equation of a Circumcircle
3.2.9Circumcircle of a Right-angled Triangle
3.3Parametric Equations (A2 only)
4Sequences & Series
4.1Binomial Expansion
5Trigonometry
5.2Trigonometric Functions
5.3Triangle Rules
6Exponentials & Logarithms
6.1Exponentials & Logarithms
7Differentiation
7.1Derivatives
7.2Graphs & Differentiation
7.3Differentiation With Trigonometry and Exponentials
7.4Rules of Differetiation (A2 only)
7.5Parametric & Implicit Differentiation
8Integration
8.1Integration
9Numerical Methods
9.1Finding Solutions
9.2Finding the Area
10Vectors
10.12D Vectors
10.23D Vectors
10.3Vector Proofs
Jump to other topics
1Proof
1.1Types of Numbers
1.2Notation
2Algebra & Functions
2.1Powers & Roots
2.2Quadratic Equations
2.3Inequalities
2.4Polynomials
2.5Graphs
2.7Transformation of Graphs
3Coordinate Geometry
3.1Straight Lines
3.2Circles
3.2.1Equations of Circles centred at Origin
3.2.2Finding the Centre & Radius
3.2.3Equation of a Tangent
3.2.4Circle Theorems - Perpendicular Bisector
3.2.5Circle Theorems - Angle at the Centre
3.2.6Circle Theorems - Angle at a Semi-Circle
3.2.7Equation of a Perpendicular Bisector
3.2.8Equation of a Circumcircle
3.2.9Circumcircle of a Right-angled Triangle
3.3Parametric Equations (A2 only)
4Sequences & Series
4.1Binomial Expansion
5Trigonometry
5.2Trigonometric Functions
5.3Triangle Rules
6Exponentials & Logarithms
6.1Exponentials & Logarithms
7Differentiation
7.1Derivatives
7.2Graphs & Differentiation
7.3Differentiation With Trigonometry and Exponentials
7.4Rules of Differetiation (A2 only)
7.5Parametric & Implicit Differentiation
8Integration
8.1Integration
9Numerical Methods
9.1Finding Solutions
9.2Finding the Area
10Vectors
10.12D Vectors
10.23D Vectors
10.3Vector Proofs
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books