1.2.3
Structure of Eukaryotic Cells
Types of Eukaryotic Cells
Types of Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells have similar structures across different types of organisms. But there are some key differences that are outlined here.


Animal cell
Animal cell
- Most animal cells have the following organelles:
- Mitochondria.
- Ribosomes.
- Endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
- Golgi.
- Lysosomes.
- Nucleus.
- Animal cells are enclosed by a cell membrane.
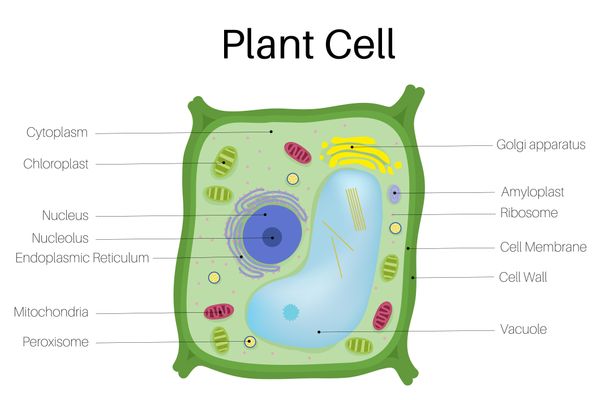

Plant cell
Plant cell
- Plant cells contain all the organelles found in animal cells.
- Plant cells also possess:
- Vacuole (a repository of cell sap).
- Chloroplasts (the site of photosynthesis).
- Cell wall (made of cellulose and contains plasmodesmata, through which cells exchange substances with each other).


Algal cells
Algal cells
- Algal cells and plant cells have an identical set of organelles.


Fungal cells
Fungal cells
- Fungal cells are similar to plant cells, apart from:
- There are no chloroplasts in fungal cells.
- The cell walls of fungal cells are made from chitin instead of cellulose.
1The Nature & Variety of Living Organisms
1.1Characteristics of Living Organisms
2Structure & Functions in Living Organisms
2.1Organisation Structure
2.1.1Cells
2.1.2Tissues
2.1.3Organs
2.1.4Organ Systems
2.1.5Organisms
2.1.6Animal cells
2.1.7Plant cells
2.1.8Cell Differentiation
2.1.9Stem Cells
2.1.10Uses of Stem Cells
2.1.11Disadvantages of Stem Cells
2.1.12End of Topic Test - Cell Types & Structures
2.1.13Exam-Style Questions - Cells
2.1.14Diffusion
2.1.15Factors affecting Diffusion
2.1.16Surface Area to Volume Ratio
2.1.17Diffusion - Experiment
2.1.18Osmosis
2.1.19Required Practical - Osmosis
2.1.20Active Transport
2.1.21Transport in Cells
2.1.22End of Topic Test - Cell Transport
2.1.23Grade 9 - Cell Transport
2.1.24Exam-Style Questions - Substance Exchange
2.2Biological Molecules
2.3Nutrition
2.3.1Photosynthesis
2.3.2Photosynthesis Equation
2.3.3Factors affecting Rate of Photosynthesis
2.3.4Photosynthesis - Calculations
2.3.5Investigating Photosynthesis
2.3.6Testing Leaves for Starch
2.3.7Grade 9 - Photosynthesis Experiment
2.3.8Exam-Style Questions - Rate of Photosynthesis
2.3.9Leaf Adaptations
2.3.10Ion Deficiencies
2.3.11Human Diet
2.3.12Vitamins and Minerals
2.3.13Dietary Needs
2.3.14Human Digestive System
2.3.15Peristalsis
2.3.16Villi
2.3.17Digestive Enzymes
2.3.18Amylase
2.3.19Protease
2.3.20Lipase
2.3.21Bile
2.3.22End of Topic Test - Enzymes & Nutririon
2.3.23Exam-Style Questions - Enzymes & Digestion
3Organism Functions
3.1Respiration
3.2Gas Exchange
3.3Transport
3.3.1Surface Area to Volume Ratio
3.3.2Exchange Surfaces
3.3.3Examples of Exchange Surfaces
3.3.4Root Hair Cells
3.3.5Transpiration
3.3.6Rate of Transpiration
3.3.7Measuring Transpiration
3.3.8Xylem
3.3.9Translocation
3.3.10Blood Components
3.3.11Plasma
3.3.12Red Blood Cell
3.3.13Platelets
3.3.14The Immune System
3.3.15Antibodies
3.3.16Vaccination
3.3.17Types of Blood Vessel
3.3.18Blood Vessels - Arteries
3.3.19Blood Vessels - Veins
3.3.20Blood Vessels - Capillaries
3.3.21Function of the Heart
3.3.22Structure of the Heart
3.3.23Heart Rate
3.3.24Heart Disease
3.3.25Double Circulatory System
3.3.26Important Blood Vessels
3.3.27End of Topic - Transport
3.3.28Exam-Style Questions - The Heart
3.4Excretion
3.5Coordination & Response
3.5.1Homeostasis
3.5.2Regulating Internal Conditions
3.5.3Coordinated Responses
3.5.4Types of Tropisms
3.5.5Auxin and Phototropism
3.5.6Nervous System
3.5.7Synapses
3.5.8Reflex Actions
3.5.9Reflex Arc
3.5.10Sense Organs
3.5.11The Eye
3.5.12Eye - Focusing
3.5.13Eye - Adapting to Light
3.5.14Thermoregulation
3.5.15Sweating and Shivering
3.5.16Thermoregulation - Blood Vessels
3.5.17Exam-Style Questions - Homeostasis
3.5.18Endocrine Glands
3.5.19Hormones
3.5.20Nervous vs Endocrine
3.5.21Adrenaline
3.5.22Glucose
3.5.23Puberty
3.5.24Menstruation
3.5.25Menstrual Cycle
3.5.26Menstrual Hormones
3.5.27Grade 9 - Hormonal Coordination
3.5.28End of Topic Test - Coordination & Response
4Reproduction & Inheritance
4.1Reproduction
4.2Genetics
4.3Variation
4.3.1Alleles
4.3.2Phenotype
4.3.3Monohybrid Inheritance
4.3.4Punnett Square
4.3.5Sex Determination
4.3.6Codominance
4.3.7Cystic Fibrosis Punnett Square
4.3.8Cystic Fibrosis Pedigree Diagram
4.3.9Variation
4.3.10Mutations
4.3.11Natural Selection
4.3.12Evolution
4.3.13Resistant Bacteria
4.3.14End of Topic Test - Variation
4.3.15Grade 9 - Evolution
4.3.16Exam-Style Questions - Cystic Fibrosis
5Ecology
5.1Ecosystems
5.1.1Ecosystems
5.1.2Resources
5.1.3Interdependence
5.1.4Growth Factors
5.1.5Assessing Ecosystems
5.1.6Quadrats
5.1.7Required Practical
5.1.8Exam-Style Questions - Sampling
5.1.9Energy Flow
5.1.10Food Chains
5.1.11Trophic Levels
5.1.12Decomposers
5.1.13Pyramids of Biomass
5.1.14Transfer of Biomass
5.1.15Reasons for Wastage
5.1.16End of Topic Test - Food and Trophic Levels
5.1.17Recycling Materials
5.1.18Carbon Cycle
5.1.19Exam-Style Questions - Carbon Cycle
5.1.20Nitrogen Cycle
5.1.21The Nitrogen Cycle and Microorganisms
5.1.22End of Topic Test - Ecosystems
5.1.23Grade 9 - Ecosystems
6Biological Resources
6.1Food Production
6.1.1Intensive Farming - Crop Yield
6.1.2Intensive Farming - Ion Deficiency
6.1.3Intensive Farming - Pest Control
6.1.4Intensive Farming - Fish Farming
6.1.5Microorganisms in Food
6.1.6Factors Affecting Microorganism Growth
6.1.7Industrial Fermentation
6.1.8Selective Breeding
6.1.9Selective Breeding Process
6.1.10Uses of Selective Breeding
6.1.11Exam-Style Questions - Selective Breeding
Jump to other topics
1The Nature & Variety of Living Organisms
1.1Characteristics of Living Organisms
2Structure & Functions in Living Organisms
2.1Organisation Structure
2.1.1Cells
2.1.2Tissues
2.1.3Organs
2.1.4Organ Systems
2.1.5Organisms
2.1.6Animal cells
2.1.7Plant cells
2.1.8Cell Differentiation
2.1.9Stem Cells
2.1.10Uses of Stem Cells
2.1.11Disadvantages of Stem Cells
2.1.12End of Topic Test - Cell Types & Structures
2.1.13Exam-Style Questions - Cells
2.1.14Diffusion
2.1.15Factors affecting Diffusion
2.1.16Surface Area to Volume Ratio
2.1.17Diffusion - Experiment
2.1.18Osmosis
2.1.19Required Practical - Osmosis
2.1.20Active Transport
2.1.21Transport in Cells
2.1.22End of Topic Test - Cell Transport
2.1.23Grade 9 - Cell Transport
2.1.24Exam-Style Questions - Substance Exchange
2.2Biological Molecules
2.3Nutrition
2.3.1Photosynthesis
2.3.2Photosynthesis Equation
2.3.3Factors affecting Rate of Photosynthesis
2.3.4Photosynthesis - Calculations
2.3.5Investigating Photosynthesis
2.3.6Testing Leaves for Starch
2.3.7Grade 9 - Photosynthesis Experiment
2.3.8Exam-Style Questions - Rate of Photosynthesis
2.3.9Leaf Adaptations
2.3.10Ion Deficiencies
2.3.11Human Diet
2.3.12Vitamins and Minerals
2.3.13Dietary Needs
2.3.14Human Digestive System
2.3.15Peristalsis
2.3.16Villi
2.3.17Digestive Enzymes
2.3.18Amylase
2.3.19Protease
2.3.20Lipase
2.3.21Bile
2.3.22End of Topic Test - Enzymes & Nutririon
2.3.23Exam-Style Questions - Enzymes & Digestion
3Organism Functions
3.1Respiration
3.2Gas Exchange
3.3Transport
3.3.1Surface Area to Volume Ratio
3.3.2Exchange Surfaces
3.3.3Examples of Exchange Surfaces
3.3.4Root Hair Cells
3.3.5Transpiration
3.3.6Rate of Transpiration
3.3.7Measuring Transpiration
3.3.8Xylem
3.3.9Translocation
3.3.10Blood Components
3.3.11Plasma
3.3.12Red Blood Cell
3.3.13Platelets
3.3.14The Immune System
3.3.15Antibodies
3.3.16Vaccination
3.3.17Types of Blood Vessel
3.3.18Blood Vessels - Arteries
3.3.19Blood Vessels - Veins
3.3.20Blood Vessels - Capillaries
3.3.21Function of the Heart
3.3.22Structure of the Heart
3.3.23Heart Rate
3.3.24Heart Disease
3.3.25Double Circulatory System
3.3.26Important Blood Vessels
3.3.27End of Topic - Transport
3.3.28Exam-Style Questions - The Heart
3.4Excretion
3.5Coordination & Response
3.5.1Homeostasis
3.5.2Regulating Internal Conditions
3.5.3Coordinated Responses
3.5.4Types of Tropisms
3.5.5Auxin and Phototropism
3.5.6Nervous System
3.5.7Synapses
3.5.8Reflex Actions
3.5.9Reflex Arc
3.5.10Sense Organs
3.5.11The Eye
3.5.12Eye - Focusing
3.5.13Eye - Adapting to Light
3.5.14Thermoregulation
3.5.15Sweating and Shivering
3.5.16Thermoregulation - Blood Vessels
3.5.17Exam-Style Questions - Homeostasis
3.5.18Endocrine Glands
3.5.19Hormones
3.5.20Nervous vs Endocrine
3.5.21Adrenaline
3.5.22Glucose
3.5.23Puberty
3.5.24Menstruation
3.5.25Menstrual Cycle
3.5.26Menstrual Hormones
3.5.27Grade 9 - Hormonal Coordination
3.5.28End of Topic Test - Coordination & Response
4Reproduction & Inheritance
4.1Reproduction
4.2Genetics
4.3Variation
4.3.1Alleles
4.3.2Phenotype
4.3.3Monohybrid Inheritance
4.3.4Punnett Square
4.3.5Sex Determination
4.3.6Codominance
4.3.7Cystic Fibrosis Punnett Square
4.3.8Cystic Fibrosis Pedigree Diagram
4.3.9Variation
4.3.10Mutations
4.3.11Natural Selection
4.3.12Evolution
4.3.13Resistant Bacteria
4.3.14End of Topic Test - Variation
4.3.15Grade 9 - Evolution
4.3.16Exam-Style Questions - Cystic Fibrosis
5Ecology
5.1Ecosystems
5.1.1Ecosystems
5.1.2Resources
5.1.3Interdependence
5.1.4Growth Factors
5.1.5Assessing Ecosystems
5.1.6Quadrats
5.1.7Required Practical
5.1.8Exam-Style Questions - Sampling
5.1.9Energy Flow
5.1.10Food Chains
5.1.11Trophic Levels
5.1.12Decomposers
5.1.13Pyramids of Biomass
5.1.14Transfer of Biomass
5.1.15Reasons for Wastage
5.1.16End of Topic Test - Food and Trophic Levels
5.1.17Recycling Materials
5.1.18Carbon Cycle
5.1.19Exam-Style Questions - Carbon Cycle
5.1.20Nitrogen Cycle
5.1.21The Nitrogen Cycle and Microorganisms
5.1.22End of Topic Test - Ecosystems
5.1.23Grade 9 - Ecosystems
6Biological Resources
6.1Food Production
6.1.1Intensive Farming - Crop Yield
6.1.2Intensive Farming - Ion Deficiency
6.1.3Intensive Farming - Pest Control
6.1.4Intensive Farming - Fish Farming
6.1.5Microorganisms in Food
6.1.6Factors Affecting Microorganism Growth
6.1.7Industrial Fermentation
6.1.8Selective Breeding
6.1.9Selective Breeding Process
6.1.10Uses of Selective Breeding
6.1.11Exam-Style Questions - Selective Breeding
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books