4.1.1
Magnets
Magnets
Magnets
Magnetism describes the ability of magnets to attract (pull towards) and repel (push away) other magnets without touching them. Every magnet creates a magnetic field around itself.


Magnets have poles
Magnets have poles
- Magnets have a north pole (N) and south pole (S).
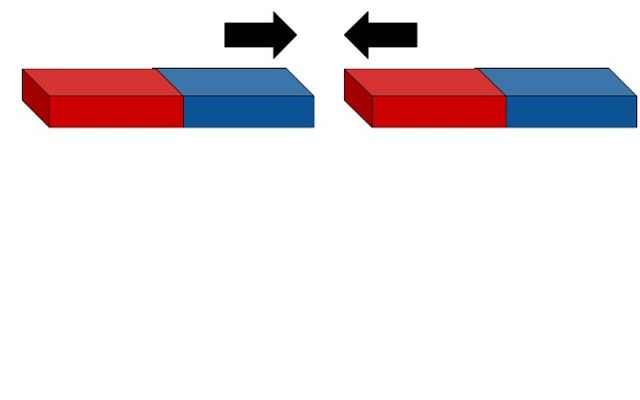

Opposite poles attract
Opposite poles attract
- Opposite poles on a magnet attract.
- The south pole of one magnet will attract the north pole of the other magnet.
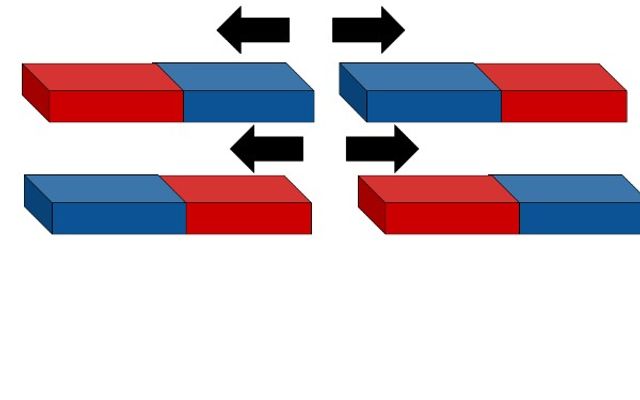

Like poles repel
Like poles repel
- Like poles on a magnet repel.
- The south pole of one magnet will repel the south pole of the other magnet.
- The north pole of one magnet will repel the north pole of another magnet.


Magnetic forces
Magnetic forces
- Every magnet creates a magnetic field around itself.
- The magnetic forces between magnets are caused by these invisible magnetic fields overlapping.
Magnets
Magnets
The key phrase to remember when thinking about magnet behaviour is: 'like poles repel, unlike poles attract'.
1Motion, Forces & Energy
1.1Physical Quantities & Measurement Techniques
1.2Motion
1.2.1Average Speed
1.2.2Calculating Average Speed
1.2.3Velocity
1.2.4Acceleration
1.2.5Distance-Time Graphs
1.2.6Speed-Time Graphs
1.2.7More Speed-Time Graphs
1.2.8Calculating Uniform Acceleration
1.2.9Gravity
1.2.10Free Fall - Distance-Time & Speed-Time Graphs
1.2.11Air Resistance
1.2.12Air Resistance - Graphs
1.2.13Optional: Calculating Acceleration
1.3Mass & Weight
1.4Density
1.5Forces: Effects of Forces
1.6Forces: Turning Effects of Forces
1.7Forces: Centre of Gravity
1.8Momentum
1.9Energy, Work, & Power: Energy
1.10Energy, Work & Power: Work
1.11Energy, Work & Power: Energy Resources
1.12Energy, Work & Power: Power
2Thermal Physics
2.1Kinetic Particle Model of Matter
2.2Thermal Properties & Temperature
3Waves
3.1General Properties of Waves
3.2Light: Reflection & Refraction
3.3Light: Thin Lenses
3.4Light: Dispersion of Light
3.5Electromagnetic Spectrum
4Electricity & Magnetism
4.1Simple Phenomena of Magnetism
4.2Electrical Quantities: Electric Charge
4.3Electrical Quantities: Electric Current
4.4Electromotive Force & Potential Difference
4.5Electrical Quantities: Resistance
4.6Electrical Energy & Electrical Power
4.7Electric Circuits: Circuit Diagrams & Components
4.8Electric Circuits: Series & Parallel Circuits
4.9Electric Circuits: Action & Use
4.10Electrical Safety
4.11Electromagnetic Effects: Electromagnetic Induction
4.12Electromagnetic Effects: The A.C. Generator
4.13Magnetic Effect of a Current
4.14Force on a Current-Carrying Conductor
4.15Electromagnetic Effects: The D.C. Motor
4.16Electromagnetic Effects: The Transformer
5Nuclear Physics
5.1The Nuclear Model of the Atom
5.2Radioactivity: Detection of Radioactivity
5.3Radioactivity: The Three Types of Nuclear Emission
6Space Physics
6.1The Earth & the Solar System
Jump to other topics
1Motion, Forces & Energy
1.1Physical Quantities & Measurement Techniques
1.2Motion
1.2.1Average Speed
1.2.2Calculating Average Speed
1.2.3Velocity
1.2.4Acceleration
1.2.5Distance-Time Graphs
1.2.6Speed-Time Graphs
1.2.7More Speed-Time Graphs
1.2.8Calculating Uniform Acceleration
1.2.9Gravity
1.2.10Free Fall - Distance-Time & Speed-Time Graphs
1.2.11Air Resistance
1.2.12Air Resistance - Graphs
1.2.13Optional: Calculating Acceleration
1.3Mass & Weight
1.4Density
1.5Forces: Effects of Forces
1.6Forces: Turning Effects of Forces
1.7Forces: Centre of Gravity
1.8Momentum
1.9Energy, Work, & Power: Energy
1.10Energy, Work & Power: Work
1.11Energy, Work & Power: Energy Resources
1.12Energy, Work & Power: Power
2Thermal Physics
2.1Kinetic Particle Model of Matter
2.2Thermal Properties & Temperature
3Waves
3.1General Properties of Waves
3.2Light: Reflection & Refraction
3.3Light: Thin Lenses
3.4Light: Dispersion of Light
3.5Electromagnetic Spectrum
4Electricity & Magnetism
4.1Simple Phenomena of Magnetism
4.2Electrical Quantities: Electric Charge
4.3Electrical Quantities: Electric Current
4.4Electromotive Force & Potential Difference
4.5Electrical Quantities: Resistance
4.6Electrical Energy & Electrical Power
4.7Electric Circuits: Circuit Diagrams & Components
4.8Electric Circuits: Series & Parallel Circuits
4.9Electric Circuits: Action & Use
4.10Electrical Safety
4.11Electromagnetic Effects: Electromagnetic Induction
4.12Electromagnetic Effects: The A.C. Generator
4.13Magnetic Effect of a Current
4.14Force on a Current-Carrying Conductor
4.15Electromagnetic Effects: The D.C. Motor
4.16Electromagnetic Effects: The Transformer
5Nuclear Physics
5.1The Nuclear Model of the Atom
5.2Radioactivity: Detection of Radioactivity
5.3Radioactivity: The Three Types of Nuclear Emission
6Space Physics
6.1The Earth & the Solar System
Unlock your full potential with Seneca Premium
Unlimited access to 10,000+ open-ended exam questions
Mini-mock exams based on your study history
Unlock 800+ premium courses & e-books