Back
Longitudinal & Transverse Waves
Transverse Waves
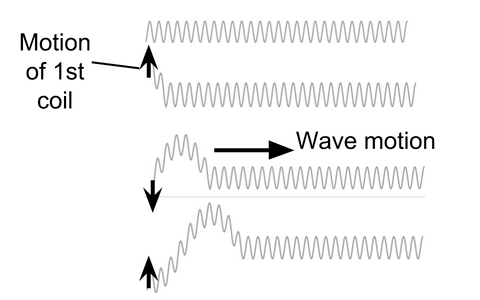
A transverse wave causes the particles in the medium (the substance that the wave travels through) to vibrate at right angles to the direction of the wave’s motion. A cork in water and the coils of a spring are examples of this. They move up and down as the wave passes.
Longitudinal Waves
A longitudinal wave causes the medium’s particles to vibrate in the same direction as the wave’s motion. Examples of longitudinal waves are sound waves and pushing a spring in and out.

Want to learn more about Longitudinal & Transverse Waves?
Join Seneca to get 250+ free exam board specfic A Level, GCSE, KS3 & KS2 online courses.





