GCSE OCR History Primer for Teachers
After interviewing 12 history teachers this year I noticed that many struggle to find enough time for setting and marking homework. There's simply not enough time to hit the perfect allocation of time between planning & preparing history classes versus setting & marking homework.
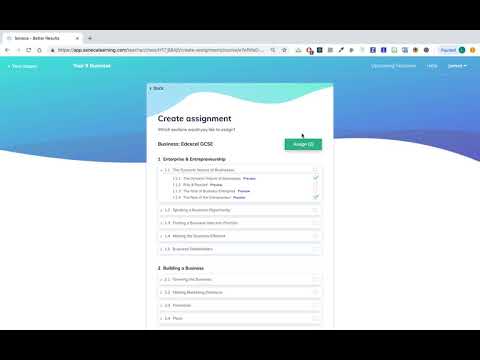
This struggle has been one of the core reasons why we decided to add a teacher platform to Seneca. Initially, only students could use the software for history revision. However, now you're able to create a class, invite your students and set homework assignments on the variety of free history courses. Besides making it possible to set homework in under 15 seconds, you can also easily track progress and identify what topic the class is struggling with, so that this can be remedied next lesson. All assignments are automatically marked and states how well each student performed per history topic such as 1.2.4 The Cuban Missile Crisis. This should save you a lot of time in setting and marking homework.
The goal of this GCSE OCR History primer is to outline which sections are covered so that you can easily add this to your lesson plan. In addition, we provide links to the core OCR history resources for GCSE teachers.
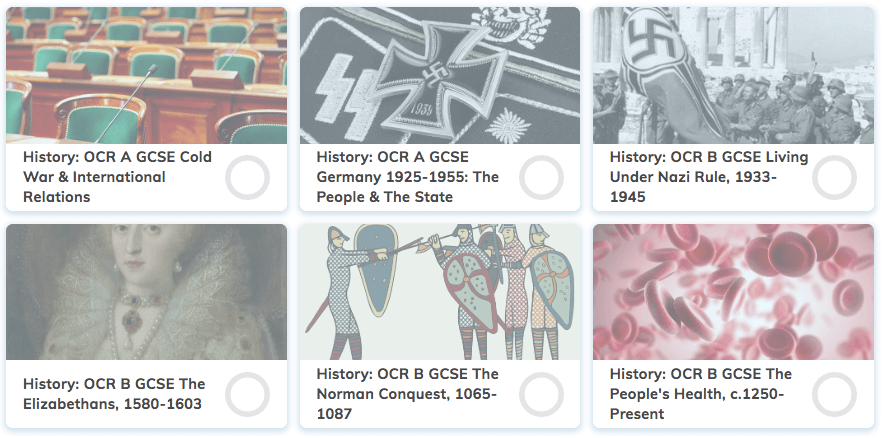
6 Free GCSE OCR Revision Courses
- Cold War & International Relations
- Germany 1925-1955: The People & The State
- Living Under Nazi Rule, 1933-1945
- The Elizabethans, 1580-1603
- The Norman Conquest, 1065-1087
- The People's Health, c.1250-Present
Vital Resources
- Seneca teacher platform
- OCR A teaching resources and exam specifications
- OCR B teaching resources and exam specifications
The Benefits for History Teachers
- Student and Teachers can use Seneca for Free.
- Exam board specific courses written by examiners and industry experts.
- Using Cognitive Neuroscience principles to study in the most effective way possible.
- Students revise more and longer due to the engagement with video's, gifs and pictures.
Setting History GCSE Homework on Seneca
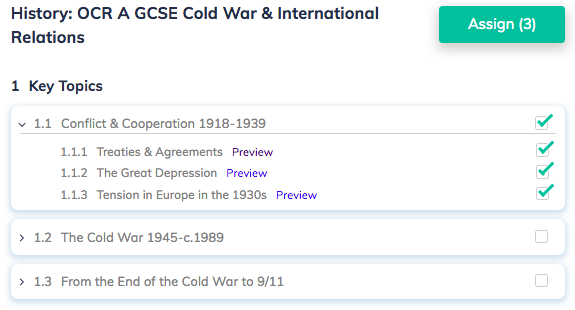
Curriculum: History: OCR A GCSE Cold War & International Relations
1 Key Topics
1.1 Conflict & Cooperation 1918-1939
1.1.1 Treaties & Agreements
1.1.2 The Great Depression
1.1.3 Tension in Europe in the 1930s
1.2 The Cold War 1945-c.1989
1.2.1 Emerging US-Soviet Rivalry
1.2.2 The Truman Doctrine & Marshall Plan
1.2.3 East-West Boundaries
1.2.4 The Cuban Missile Crisis
1.2.5 Cold War Conflicts
1.3 From the End of the Cold War to 9/11
1.3.1 Reagan & Gorbachev
1.3.2 Consequences of the Soviet War in Afghanistan
2 Changing Interpretations
2.1 Changing Interpretations
2.1.1 Appeasement
2.1.2 The Responsibility for Cold War Tensions
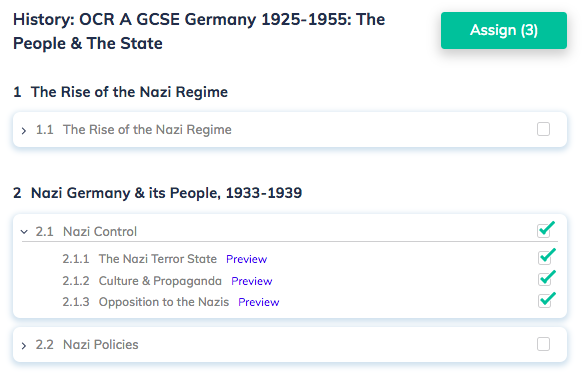
Curriculum: History: OCR A GCSE Germany 1925-1955: The People & The State
1 The Rise of the Nazi Regime
**1.1 The Rise of the Nazi Regime **
1.1.1 Weimar Republic
1.1.2 Germany & the Great Depression
1.1.3 The Rise of the Nazis
1.1.4 Nazi Consolidation of Power
2 Nazi Germany & its People, 1933-1939
2.1 Nazi Control
2.1.1 The Nazi Terror State
2.1.2 Culture & Propaganda
2.1.3 Opposition to the Nazis
2.2 Nazi Policies
2.2.1 Economic
2.2.2 Women & Youth
2.2.3 Racial Beliefs & Policies
2.2.4 Persecution of the Jews
3 War & Its Legacy, 1939-1955
3.1 Germany in WWII
3.1.1 Outbreak of War
3.1.2 Impact of War
3.1.3 Opposition During the War
3.1.4 Final Solution
3.2 Germany after WWII
3.2.1 Defeat & Occupation
3.2.2 East vs West Germany
Curriculum: History: OCR B GCSE Living Under Nazi Rule, 1933-1945
1 Dictatorship
1.1 Hitler & The Nazi Party in 1933
1.1.1 Hitler & The Growth of the Party
1.2 Establishing Dictatorship, 1933-1934
1.2.1 Establishing Dictatorship
1.2.2 Achieving Total Power, July 1933 - August 19342Control & Opposition
2.1 The Machinery of Terror
2.1.1 Police State & Legal System
2.1.2 The Gestapo & SS
2.1.3 Concentration Camps
2.2 Nazi Propaganda
2.2.1 The Effectiveness of Nazi Propaganda
2.3 Opposition to Nazi Rule
2.3.1 The Left
2.3.2 Church Leaders
2.3.3 Youth Groups
2.3.4 Support for Nazi Rule
3 Changing Lives, 1933-1939
3.1 Work & Home
3.1.1 Work
3.1.2 Home
3.2 The Lives of Young People
3.2.1 Education
3.2.2 Youth Movements
3.3 Nazi Racial Policy
3.3.1 Racial Policy
3.3.2 Persecution of the Jews
4 Germany in War
4.1 The Impact of War
4.1.1 Impact of the War Economy on the People
4.1.2 Impact of Total War on the People
4.2 Growing Opposition from the German People
4.2.1 Opposition from the People
4.2.2 Opposition from the Army
5 Occupation
5.1 Nazi Rule in Eastern and Western Europe5.1.1Western Europe
5.1.2 Eastern Europe
5.2 The Final Solution
5.2.1 Ghettos & Executions
5.2.2 Death Camps
5.3 Responses to Nazi Rule
5.3.1 Collaboration
5.3.2 Accommodation
5.3.3 Resistance
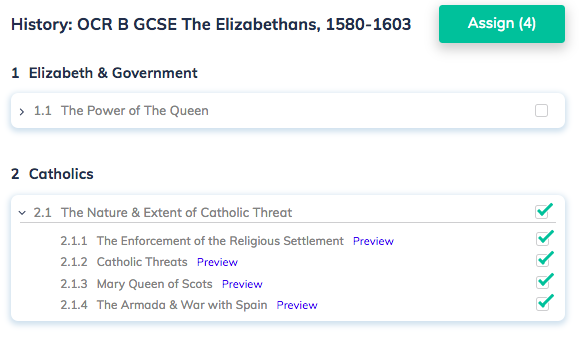
Curriculum: History: OCR B GCSE The Elizabethans, 1580-1603
1 Elizabeth & Government
1.1 The Power of The Queen
1.1.1 Elizabeth & Her Court
1.1.2 Elizabeth & Her Parliaments
1.1.3 Elizabeth & Her People
2 Catholics
2.1 The Nature & Extent of Catholic Threat
2.1.1 The Enforcement of the Religious Settlement
2.1.2 Catholic Threats
2.1.3 Mary Queen of Scots
2.1.4 The Armada & War with Spain
3 Daily Lives
3.1 The Nature & Dynamics of Elizabethan Society
3.1.1 The Nature & Structure of Society
3.2 Contrasting Lives
3.2.1 People's Lives
3.2.2 Family Life
3.2.3 Poverty in Elizabethan TImes
4 Popular Culture
4.1 Merry England
4.1.1 Theatres
4.1.2 Other Pastimes
4.2 The Persecution of Witches
4.2.1 The Persecution of Witches
5 The Wider World
5.1 England's Connections with the Wider World
5.1.1 Imperial Ambitions
5.1.2 American Colonies
5.1.3 Trade
Curriculum: History: OCR B GCSE The Norman Conquest, 1065-1087
1 England On The Eve Of Conquest
1.1 The Nature & Structure of Anglo-Saxon England
1.1.1 Anglo-Saxon Society
1.1.2 Anglo-Saxon Religion
1.1.3 Anglo-Saxon Culture
2 Invasion & Victory
2.1 How & Why Did William of Normandy Become King?
2.1.1 Norman Society pre-1066
2.1.2 The Succession Crisis of 1066
2.1.3 The Battles
3 Resistance & Response
3.1 The Establishment of Norman Rule
3.1.1 First Uprisings Against Norman Rule
3.1.2 Northern Resistance & the Harrying of the North
3.1.3 Hereward's Rebellion & Aftermath
4 Castles
4.1 The Nature & Purpose of Norman Castles
4.1.1 Pre-Conquest & Early Norman Castles
4.1.2 Distribution & Design of Norman Castles
5 Conquest & Control
5.1 The Impact of the Norman Conquest on Society
5.1.1 Domesday Book
5.1.2 Social Structure of Norman England
5.2 Change & Continuity
5.2.1 Language
5.2.2 Laws
5.2.3 Church
Curriculum: History: OCR B GCSE The People's Health, c.1250-Present
1 Medieval Britain c.1250-c.1500
1.1 The Features of Medieval Britain
1.1.1 Living Conditions
1.1.2 Responses to the Black Death
1.1.3 Approaches to Public Health
1.1.4 Medicine, Monasteries & the Church
2 Early Modern Britain c.1500-c.1750
2.1 Cultural, Social & Economic Change
2.1.1 Social Change & the Growth of Towns
2.1.2 Cultural & Economic Change
2.1.3 Changing Living Conditions
2.2 Responses to Outbreaks of Plague
2.2.1 The Great Plague
2.3 Government & Public Health
2.3.1 Local & National Government
2.3.2 The Urban Environment
2.3.3 The Gin Craze, 1660-1751
3 Industrial Britain, c.1750-c.1900
3.1 Industrialisation
3.1.1 The Growth of Major Cities
3.1.2 Political Changes
3.2 Urban Living Conditions
3.2.1 Housing, Food & Waste
3.2.2 Responses to Cholera
3.3 Public Health Reform in the 19th Century
3.3.1 Public Health Acts
4 Britain since c.1900
4.1 Economic, Political, Social & Cultural Change
4.1.1 Social & Political Change
4.2 Living Conditions & Lifestyles
4.2.1 Living Conditions
4.2.2 New Diseases and Treatments
4.3 Responses to Epidemics
4.3.1 Spanish Influenza & AIDS
4.4 Government Involvement in Public Health
4.4.1 The NHS
4.4.2 Public Health Campaigns
5 Themes in Public Health c.1250 - Present
5.1 The Impact of Living Conditions on People's Health
5.1.1 Change & Continuity
5.2 The Response to Epidemics
5.2.1 Change & Continuity
5.3 Attempts to Improve Public Health
5.3.1 Change & Continuity