Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis takes place inside chloroplasts found in plants and algae. The reaction is endothermic, meaning that it requires energy. The source of this energy is sunlight, which is trapped by a chemical called chlorophyll inside chloroplasts in plant cells. During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide reacts with water to produce glucose and oxygen.
The Rate of Photosynthesis
The four key factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis are:
- Chlorophyll concentration - High chlorophyll concentration gives a high rate of photosynthesis.
- Light intensity - Increasing light intensity increases the rate of photosynthesis because more energy is provided. However, if the light intensity is increased above a certain threshold, the rate of photosynthesis will not increase because another factor (such as temperature) is limiting the rate of the reaction.
- Carbon dioxide concentration - Increasing the carbon dioxide concentration increases the rate of photosynthesis because carbon dioxide is a reactant in photosynthesis. However, above a certain threshold, further increases in the carbon dioxide concentration do not increase the rate of photosynthesis because another factor (such as light intensity) is limiting the rate of reaction.
- Temperature - Increasing the temperature increases the rate of photosynthesis because more energy is provided. However, if the temperature is increased to above about 45°C, the enzymes that catalyse (speed-up) the reaction begin to denature (not work anymore). This causes the rate of the reaction to drop sharply until it stops altogether.
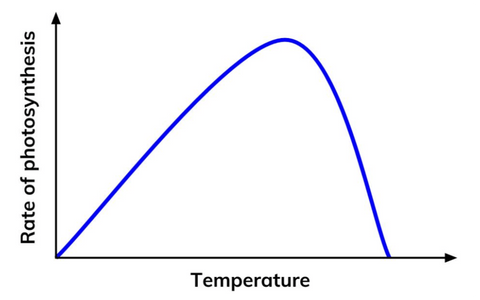
Initially, increasing temperature increases the rate of photosynthesis, as more energy is provided. Above a certain temperature (about 45 degrees Celsius), the enzymes involved in the reaction begin to denature and, consequently, the rate of the reaction begins to drop sharply until it stops altogether.
Want to learn more about Photosynthesis?
Join Seneca to get 250+ free exam board specfic A Level, GCSE, KS3 & KS2 online courses.





